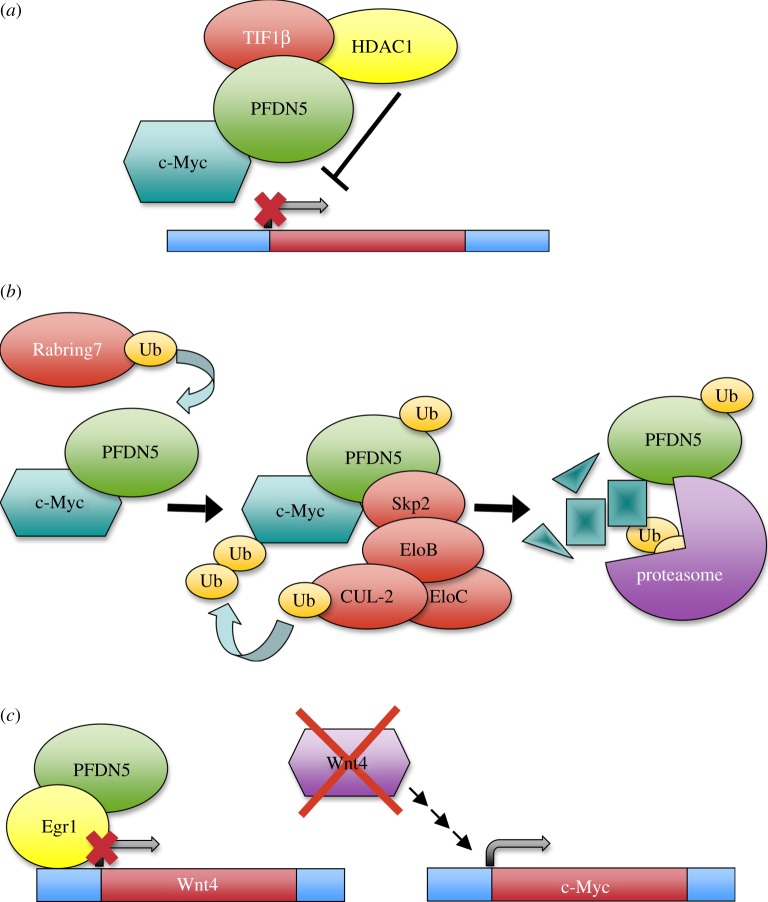
Figure 3.
Human PFDN5 is involved in three different control mechanisms of c-Myc. (a) PFDN5 binds the N-terminal region of c-Myc, and represses its transcriptional activity by recruiting the TIF1β correpressor and the histone deacetylase HDAC1–mSin3 complex. (b) PFDN5 drives c-Myc into proteasome-dependent degradation by recruiting the ubiquitin ligase Skp2–ElonginC–ElonginB–Cullin2 complex. PFDN5 mono-ubiquitination, which is induced by Rabring7, stimulates this process. (c) PFDN5 and Egr1 cooperate in the transcriptional repression of Wnt4, which is one of the elements of the Wnt-β-catenin pathway that positively controls the c-Myc gene.