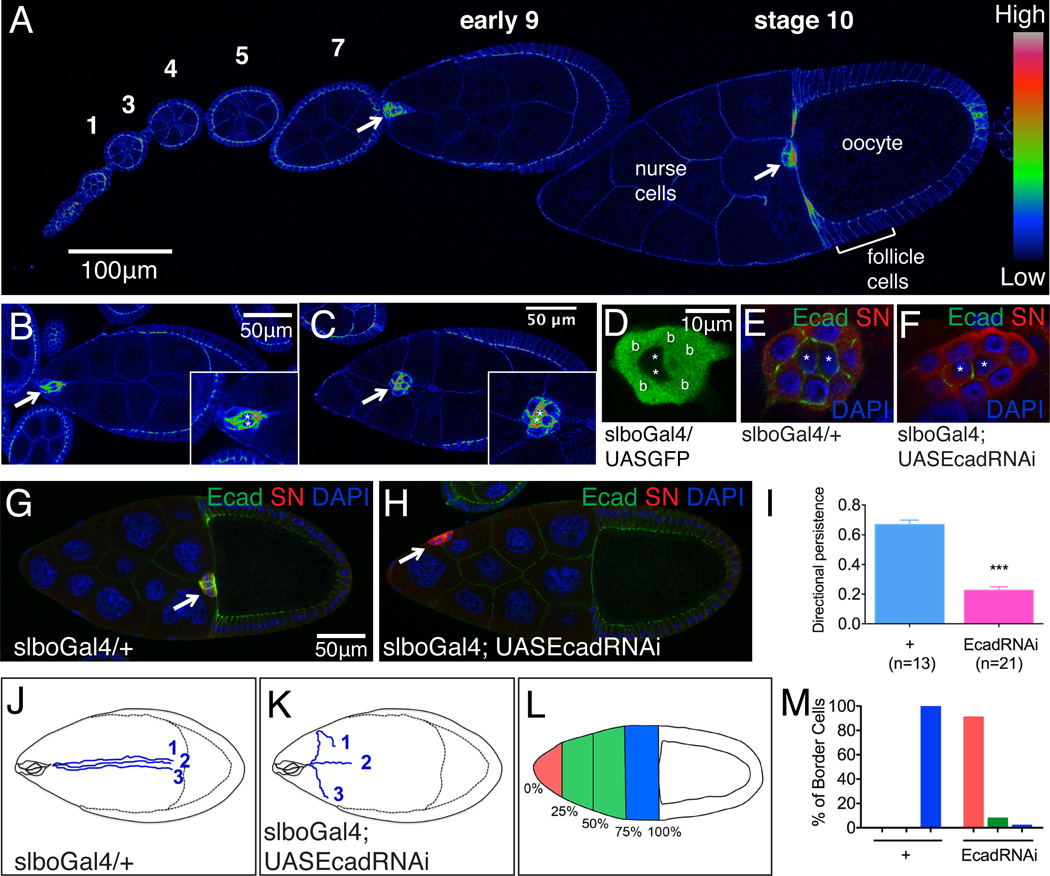
Figure 1. E-cadherin expression and k.d. phenotypes in border cells.
(A-C) E-cadherin antibody staining. (A) One ovariole with stages 1-10 of egg chamber development. Early (B) and mid (C) stage 9 egg chambers. Images are pseudo-colored (using Rainbow RGB in Image J) to emphasize spatial differences in E-cadherin concentration. Arrows indicate border cell clusters. Insets show magnified views. Asterisks mark polar cells. (D-F) Specific inhibition of E-cadherin in outer, migratory cells. (D) slboGal4-driven expression of GFP in outer migratory cells, not polar cells (*). (E) Normal expression of E-cadherin (Ecad, green) in border cells and polar cells. (F) Inhibition of Ecad expression by slboGal4 driven RNAi in outer border cells, not polar cells (*). In E and F, nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue) and cytoplasm with Singed (SN) antibody (red). (G) WT stage 10 egg chamber showing normal migration of border cells (arrow) to the oocyte. (H) Abnormal position of border cells (arrow) following inhibition of Ecad expression by slboGal4 driven RNAi. (I) Directional persistence values calculated from movies. Genotypes are slboGal4; UAS-dsRed, UASmCD8 GFP with or without UAS EcadRNAi. ***p<0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (J-K) Diagrams showing three representative traces of migration paths from movies of WT (J) and Ecad RNAi border cell clusters (K). (L-M) Histogram showing the spatial distribution of border cells in stage 10 egg chambers from slboGal4 females with or without UASEcadRNAi.