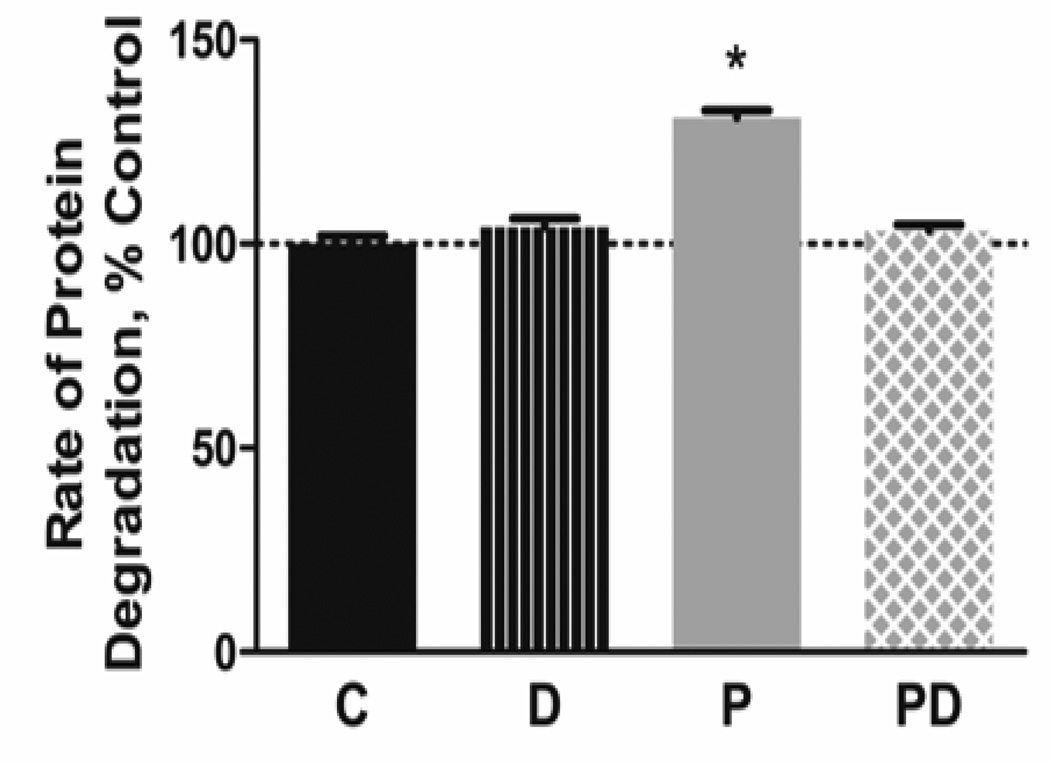
Figure 1.
Docosahexaenoic acid prevents palmitate-induced protein degradation. C2C12 myotubes were pre-labeled with 14C-phenylalanine then treated with 500 µmol/L palmitate (PA) and/or 100 µmol/L docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) for 28 h. The rate of protein degradation was calculated by measuring the release of 14C-phenylalanine into the culture media. PA increased the rate of protein degradation, while co-treatment with DHA prevented the response. Representative results from 1 of 3 independent experiments are shown (*p<0.01 versus other groups, n=6 per group per experiment)