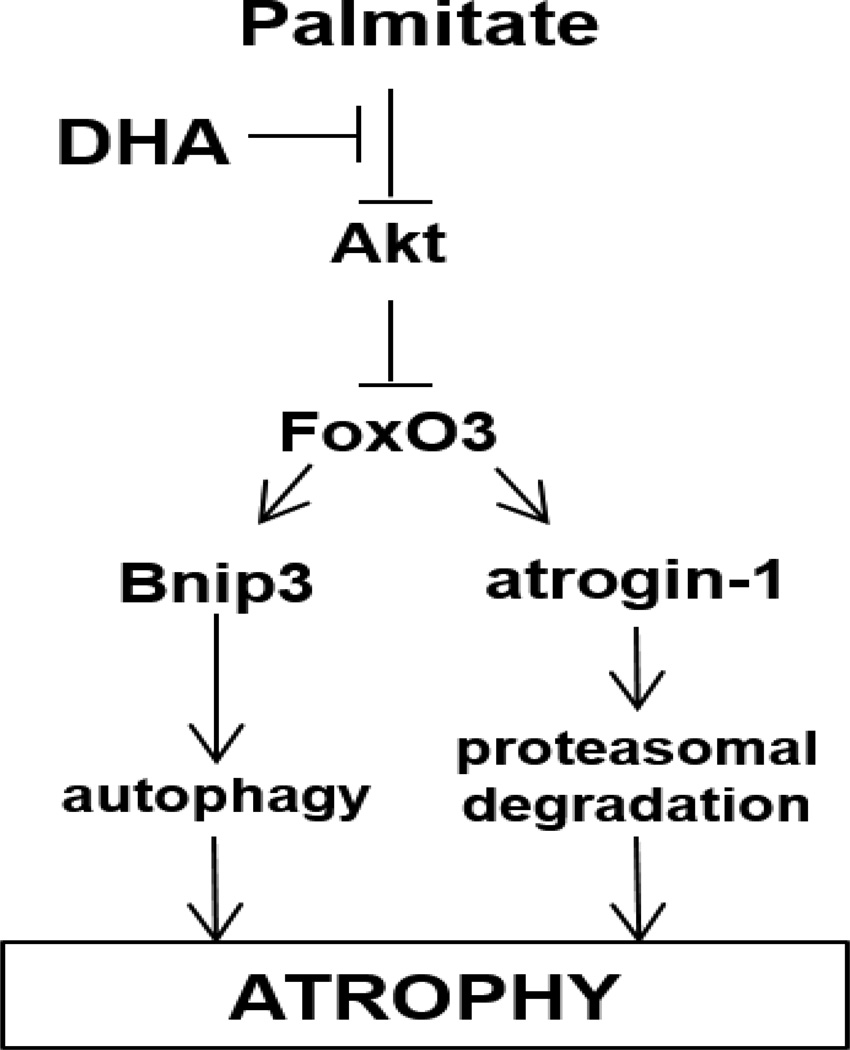
Figure 6.
The Akt/FoxO3 axis is a key regulator of the activity of various proteolytic pathways in muscle cells, including the ubiquitin-proteasome and macroautophagy systems. Palmitate induces the activity of multiple proteolytic systems, resulting in myotube atrophy. DHA counteracts the effects of palmitate by restoring Akt activation and FoxO3 inhibition, thus preventing the upregulation of protein degradation.