Figure 5.
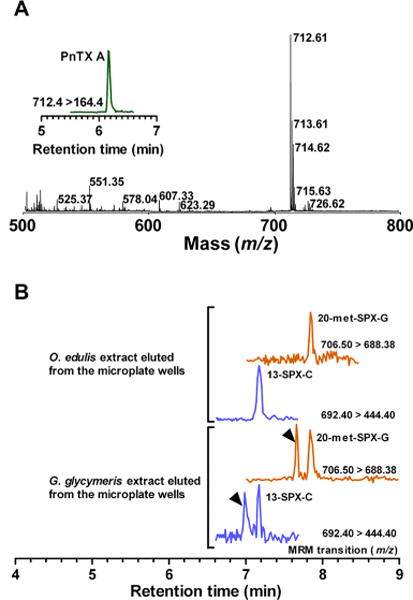
Coupling of the microplate-receptor binding assay with mass spectrometry methods. (A) Torpedo-electrocyte membranes were incubated with cyclic imine toxin standards. Following a wash step, bound toxins were eluted from the wells with methanol and analyzed by MALDI-TOF MS. Full scan, m/z 500–800, showing the protonated molecular ion of pinnatoxin-A (m/z 712.61) eluted from microplate wells. Inset: MRM analysis of pinnatoxin-A eluted from microplate wells. (B) UPLC-MS/MS analysis of O. edulis and G. glycymeris extracts eluted from microplate wells. Torpedo-electrocyte membranes were incubated with O. edulis and G. glycymeris extracts. Following a wash step, bound toxins were eluted from the wells with methanol and analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS: 20-Methyl spirolide-G and 13-desmethyl spirolide-C were detected in both shellfish samples. Note that isomers of 20-methyl spirolide-G and 13-desmethyl spirolide-C were also retrieved in eluted samples from G. glycymeris extract.
