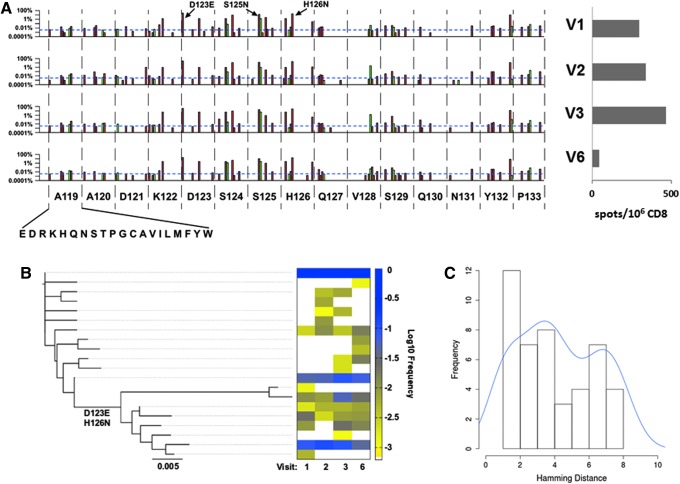
FIG. 4.
AQ9/NP10 epitope focus reveals active CTL selection and insight into population-level genetic dynamics. (A) High-resolution focus on substitutions observed in the Gag epitope AQ9/NP10 from amino acids 119–133 by visit time point. The y-axis is in log percentage, with the blue horizontal dotted line showing the sensitivity cutoff (0.0034%), and silent versus missense mutations shown in green and red, respectively. Interferon (IFN)-γ ELISpot confirmation of patient CTL targeting AQ9/NP10 using consensus subtype B Gag peptide (117–131), with the number of positive spots/106 CD8 at 298.5, 340, 468, and 43 for V1–V3 and V6, respectively. (B) Neighbor-joining tree constructed using AQ9/NP10 containing amplicon 4 using all 20 haplotypes with a maximum occurrence frequency of >0.1% showing two distinct clusters distinguished by the key variants D123E and H126N. The corresponding heat map shows the haplotype frequency at each visit time point at log10 frequency from yellow (low frequency) to blue (high frequency). (C) Pairwise Hamming distances for the haplotypes detected in V1 showing a bimodal distribution indicating two or more ancestral viruses are required prior to V1 to generate the distinct phylogenetic viral clusters observed.