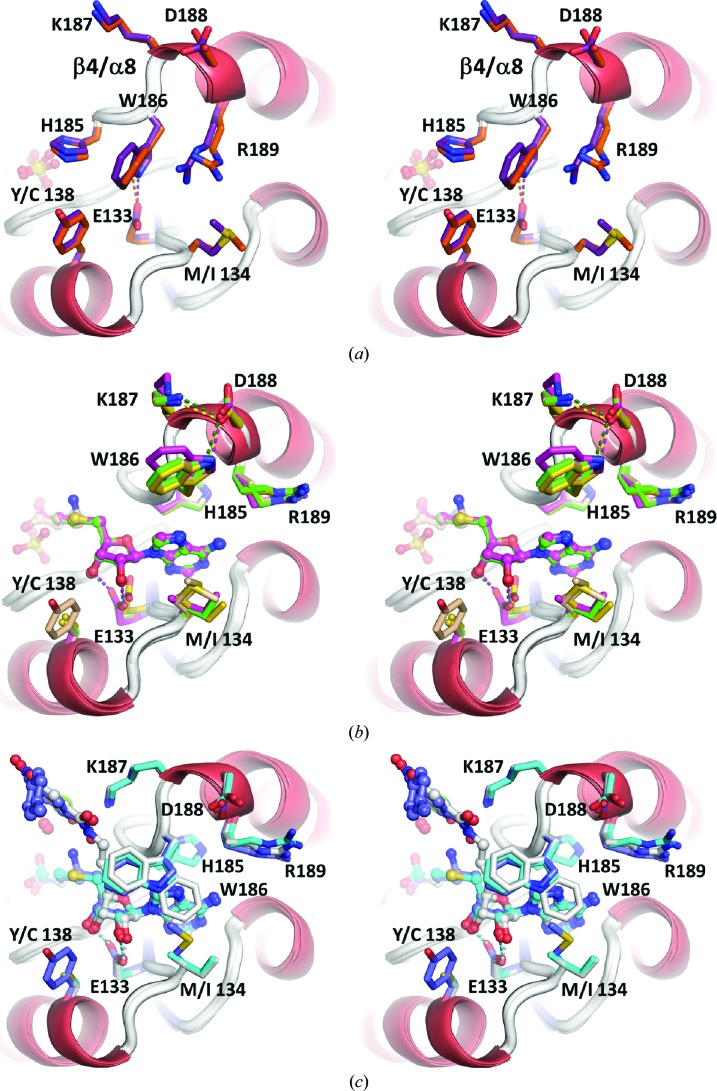
Figure 5.
Stereoviews of conformational changes in the adenine site of rat COMT. (a) The two apo COMT structures (5) (orange) and (6) (violet) and a previously determined rat COMT structure (grey; PDB entry 2zlb; Tsuji et al., 2009 ▶) have the same side-chain conformations in the adenine site. The structures have phosphate or sulfate bound at the site where the carboxylate group of SAM normally binds. Trp186 occupies roughly the usual position of the adenine base and hydrogen-bonds to Glu133, which normally binds the ribose hydroxyl groups. His185 is swung out by 7.4 Å (Cγ atom distance) relative to its position when substrate is bound and packs perpendicularly onto the indole ring of Trp186. The other side of the indole ring is contacted by Arg189. (b) The half-closed conformation is adopted by four COMT structures: (7) (sinefungin, wheat), (9) (sulfate, yellow), (10) (SAH, green) and (11a) (SAH, magenta). Asp188 hydrogen-bonds to the indole N atom of Trp186, keeping it from packing on top of the adenine base. Lys187 is in the out-conformation away from the Mg2+ site and interacts electrostatically with Asp188. His185 has swung over to the other side and is buried under the adenine base in a previously observed perpendicular interaction of the aromatic groups. Also, Arg189 has swung out of the adenine site. Structure (9) is notable because the half-closed conformation is adopted in the absence of a compound in the adenine site. (c) The closed conformation is adopted by two novel COMT structures (8) (sinefungin/tolcapone, blue) and (11b) (SAH, cyan). This is the standard conformation of substrate-bound COMT that is also adopted in bisubstrate-inhibitor complexes. As a reference PDB entry 3oe4 (Ellermann et al., 2011 ▶) is shown (grey). Asp188 adopts another rotamer and releases both Lys187 and Trp186. Trp186 now packs perpendicularly on top of the adenine base and the catalytic Lys187 is in the in-conformation towards the Mg2+ site.