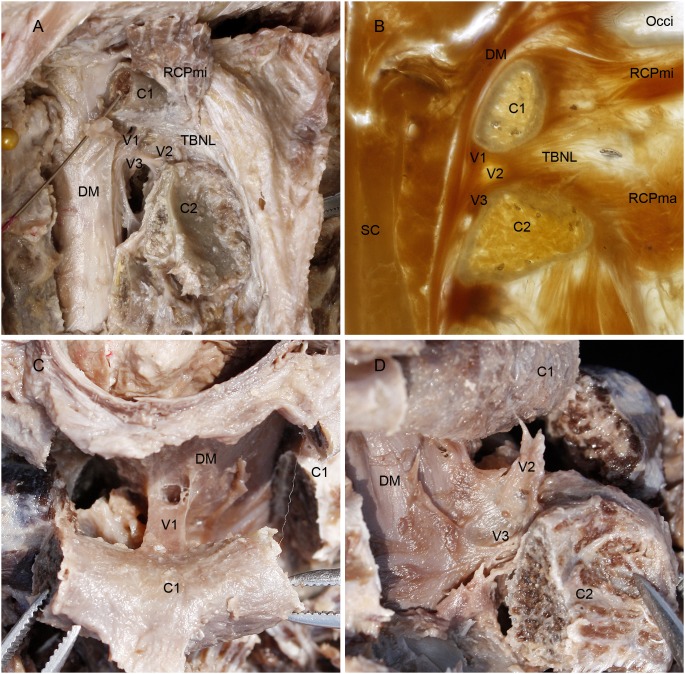
Figure 2. Vertebrodural Ligaments as shown in the dissected specimens and the P45 sheet plastination.
A: Posterolateral aspect of the superior cervical vertebral canal; B: Median sagittal P45 plastination sheet of the superior cervical vertebral canal; C: Superior aspect of the dura mater and the posterior arch of atlas; D: Posterolateral aspect of the dura mater and the atlantoaxial interspace. On dissecting the posterior arch of the atlas and the lamina of the axis bilaterally and reflecting from one side to another (A), the vertebrodural ligament (VDL) was exposed in the posterior epidural space, which connected the dura matter with the atlas, axis and atlantoaxial space, thus the VDL was subdivided into three parts: the atlantal part, the TBNL’s part and the axial part (A). The median sagittal P45 plastination sheet of the superior cervical vertebral canal also showed that VDL consisted of these three parts (B). These three parts of VDL merged with each other and ran down almost vertically in the posterior epidural space continuing to the dura mater just anterior to the lamina of the axis (A, B). When the posterior arch of the atlas was cut bilaterally and reflected posteriorly, the atlantal part of VDL was shown specially in superior aspect, which was coronally banded in shape (C). When the lamina of the axis was cut bilaterally and then reflected posteroinferiorly, the TBNL’s and axial parts of VDL were shown in a lateral view to protrude from the dura mater in the median sagittal position and extending to the atlantoaxial interspace and the lamina of axis (D). VDL, the vertebrodural ligament. V1, atlantal part. V2, TBNL’s part. V3, axial part. RCPmi, rectus capitis posterior minor; C1, posterior arch of atlas; TBNL, to be named ligament; C2, lamina of vertebral arch of axis; DM, dura mater; Occi, occipital bone; SC, spinal cord.