Figure 2. Expression, purification, and enzymatic activity of recombinant SID protein.
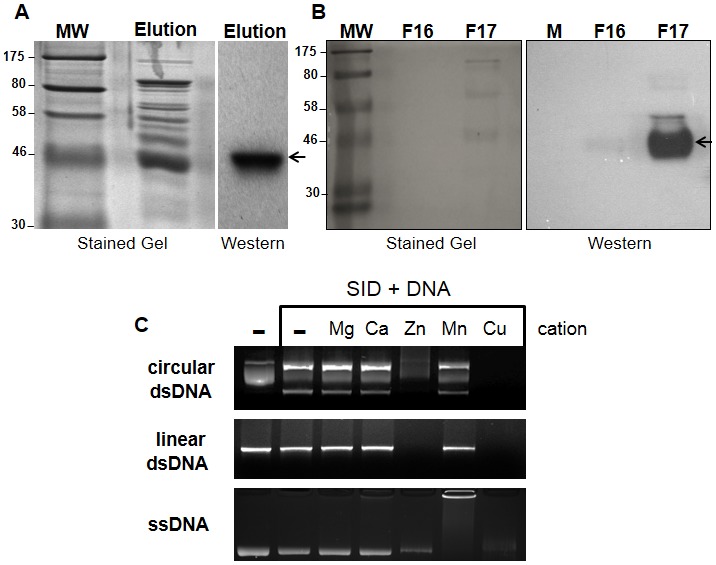
(A) Histidine (6x) tagged SID protein expressed in bacteria was partially purified by immobilized nickel affinity chromatography. The partially purified fraction containing the SID protein (Elution) was subjected to SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and either stained in situ or transferred to a membrane (samples separated in duplicate) and hybridized with anti-Histidine antibodies. The recombinant SID protein was readily detected in the fraction containing 250 mM imidazole (see arrow). (B) Purification of the partially purified protein (from A) by size exclusion chromatography (Superose 12). After separation, the eluted SID protein was primarily detected in a single fraction (F 17; 1 ml) with anti-Histidine antibodies (arrow) as in part A. Molecular weight markers (MW; in kDa) are shown on the left side of gels. (C) Nuclease activity of partially purified (F 17) fraction on nucleic acid templates in the presence of common cations (1 mM). Circular plasmid double stranded (ds) DNA was degraded extensively in the presence of Cu++ and Zn++ but not when the enzyme was incubated along with other cations or in the absence of cation (–). The plasmid DNA contained supercoiled (middle band), nicked circular (top band) and linear DNA (bottom band). Degradation of linear DNA and single stranded DNA was also observed only in the presence of Cu++ and Zn++. All reactions were carried out for 2 hr at 37°C.
