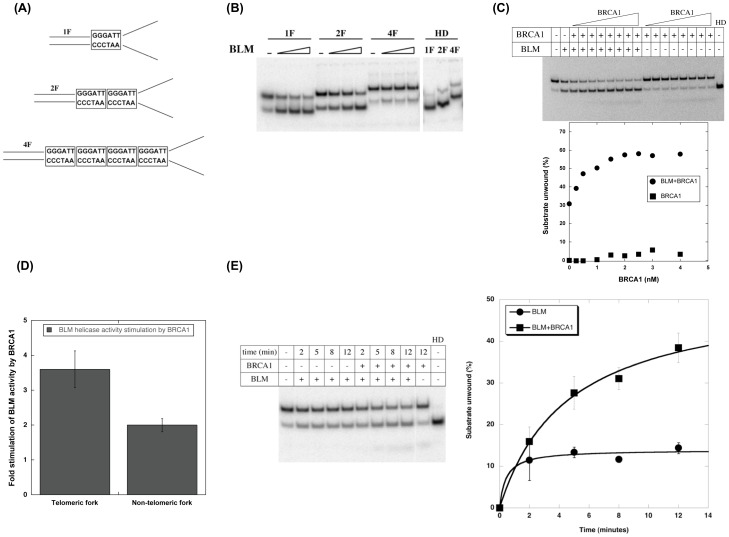
Figure 9. BRCA1 stimulates BLM helicase activity on telomeric repeat forks.
(A) Fork substrates (1F, 2F and 4F) used for the study. The number of telomeric repeat units (GGGATT) are boxed in each fork substrate – 1F contains one repeat, 2F contains two repeats and 4F contains four repeats. (B) BLM helicase activity on fork substrates. Increasing amounts of BLM (0.6 nM, 1.2 nM and 4.2 nM) were used for each substrate, reactions were terminated after 12 minutes and analyzed by native PAGE. HD refers to heat-denatured substrate. (C) Effect of BRCA1 on BLM helicase activity on 2F substrate. Helicase reactions were performed for 12 minutes with 1.2 nM BLM and increasing concentrations of BRCA1 (0–4 nM). Reactions were terminated and analyzed by native PAGE. The amount of substrate unwound (%) was plotted as a function of BRCA1 (nM). A representative gel and corresponding graph are shown. (D) Stimulation of BLM activity by BRCA1 on telomeric and non-telomeric substrates. BLM helicase activity was tested in the presence of 3 nM BRCA1 on fork substrates that contained two telomeric repeats (panel A) or a non-telomeric sequence instead of the repeat units. Reactions were analyzed by native PAGE and quantitated on a phosphorimager. The fold stimulation of BLM activity by BRCA1 for each substrate is shown as histogram. (E) BRCA1 enhances the rate of unwinding of telomeric fork by BLM. Kinetics of BLM unwinding was analyzed in the presence of 1.2 nM BLM and 3 nM BRCA1. Reactions were analyzed as in C. The amount of substrate unwound (%) was plotted as a function time (minutes) and fitted to Michaelis-Menton kinetics using Kaleidagraph. A representative gel and corresponding graph are shown.