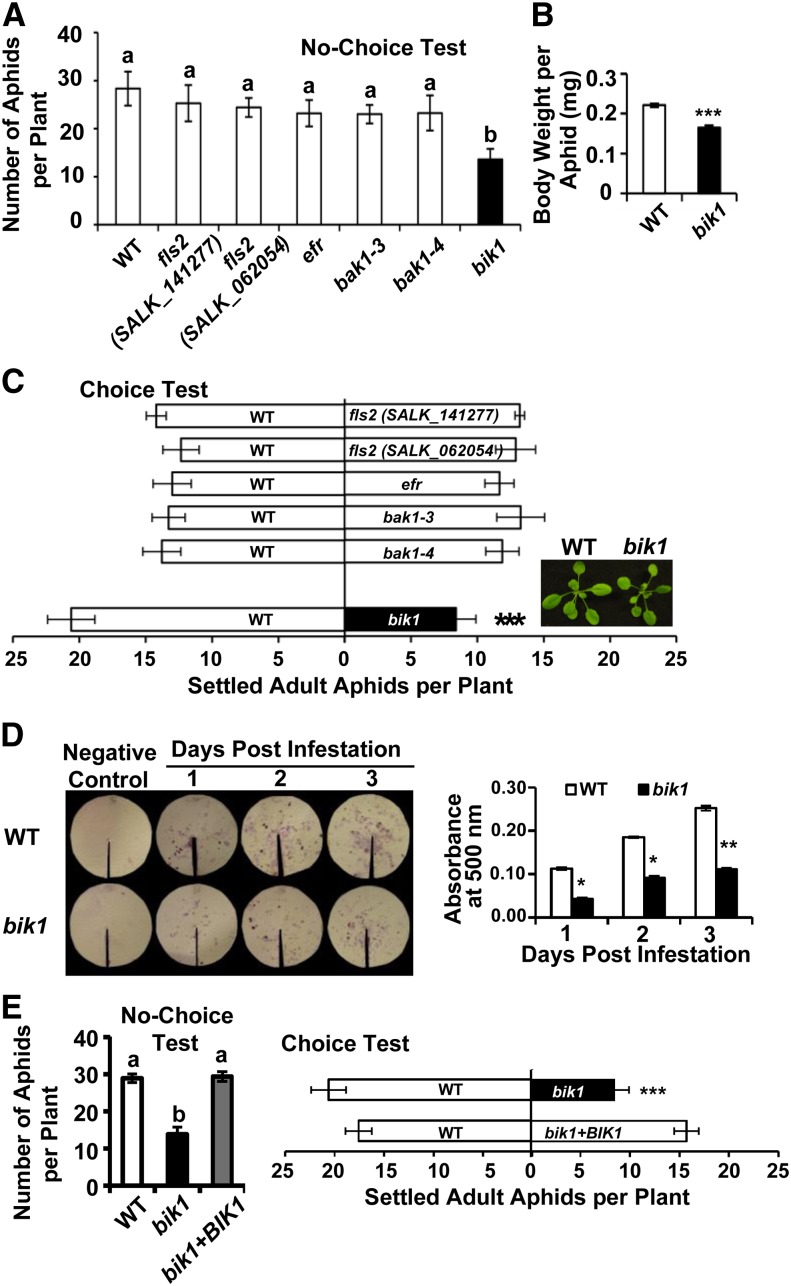
Figure 1.
Loss of BIK1 function confers resistance to green peach aphids. No-choice tests (A) and aphid body weight (B) of indicated genotypes. For no-choice tests, six second-instar nymphs were inoculated on each plant (4-5 weeks old). Total aphid numbers were recorded 7 d later. At least 10 replications were performed for each genotype. To obtain average body weight of adult aphids, neonates were reared on the wild type (WT) or bik1 for 10 d. Adults were then collected and were weighed as six groups of 10 aphids each. C, Choice tests. Three-week-old plants were used. At this developmental stage, no apparent size differences were observed between genotypes including the wild-type versus bik1 pair. Settled aphids were counted 6 h after releasing 35 adults in between two plants of the tested genotypes. Each test was comprised of 10 replicates. Inset image of the shoot phenotypes of the 3-week-old, uninfested wild type and bik1. D, Aphids on bik1 excreted less honeydew than those reared on the wild type. Quantity of honeydew secretion was correlated with the area and intensity of ninhydrin stains (left) and with optical density at 500 nm values (right). E, Expression of BIK1 cDNA confers wild-type levels of aphid susceptibility to bik1. One-way ANOVA was applied to no-choice tests, and the χ2 test was used to analyze data derived from choice tests. Body weight and honeydew secretion data were analyzed by independent samples’ Student’s t tests. Bars represent means ± se. Statistical significance for treatment effects is marked *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, or ***P < 0.001. Means with different letters were significantly different (P < 0.05).