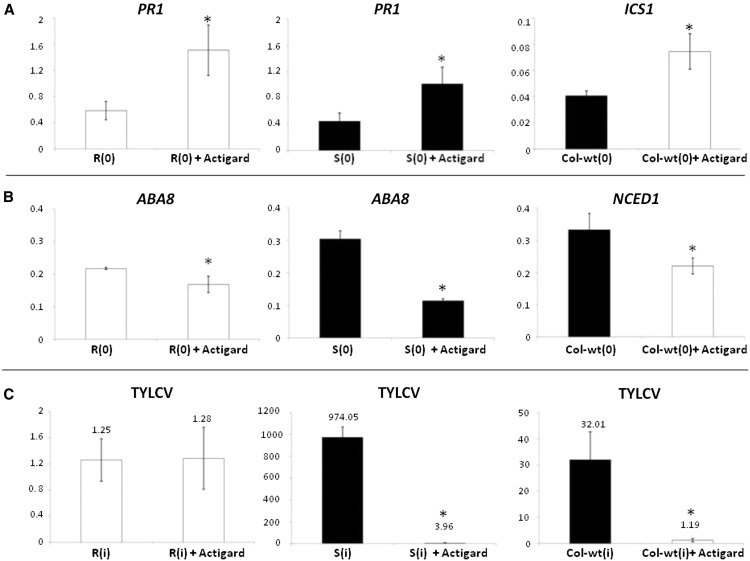
Figure 6.
Effects of acibenzolar-S-methyl (Actigard) on the expression of hormone marker genes (SA: PR1 and AtICS1 and ABA: ABA8 and AtNCED1) and on resistance to TYLCV in R and S tomato and wild-type Arabidopsis plants. A and B, qPCR analysis of hormone-related marker or biosynthesis genes associated with SA (A) and ABA (B) in uninfected tomato and Arabidopsis plants (0 dpi) that had or had been treated with Actigard, as compared with untreated control plants. The tomato β-actin gene and the Arabidopsis Actin2 or UBQ10 genes were used as calibrators. C, qPCR estimation of relative amounts of TYLCV in infected, Actigard-treated tomato and Arabidopsis plants at 7 dpi as compared with untreated control plants. The numbers above the columns represent the values. Data points are means ± se (n = 4–10). Asterisk indicates a significant difference (Student’s t test, P < 0.05).