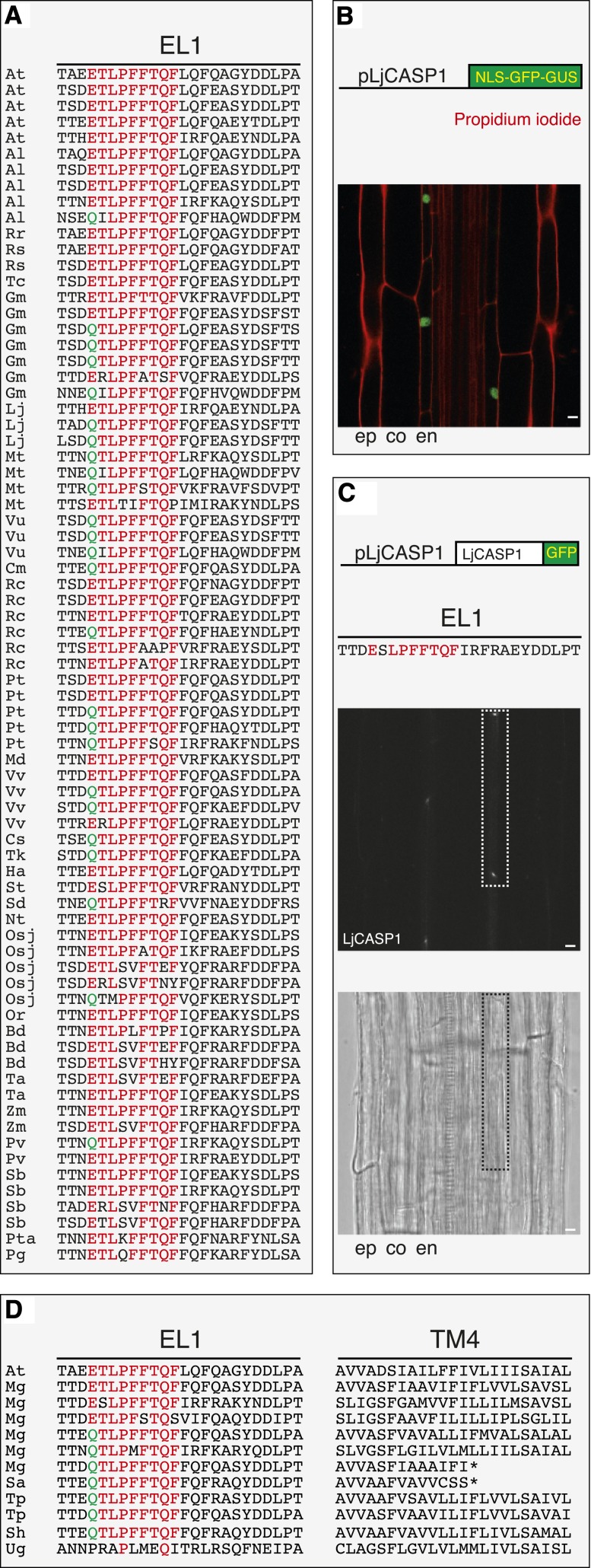
Figure 3.
The AtCASP first extracellular loop is conserved in euphyllophytes. A, EL1 of AtCASP1 is aligned to potential functional homologs. The nine-amino acid signature specific to AtCASPs and absent in AtCASPLs is highlighted in red. In the first position, E (red) and Q (green) are both found. Species abbreviations are as follows: At, Arabidopsis; Al, Arabidopsis lyrata; Rr, Raphanus raphanistrum; Rs, Raphanus sativus; Tc, Theobroma cacao; Gm, Glycine max; Lj, Lotus japonicus; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Vu, Vigna unguiculata; Cm, Cucumis melo; Rc, Ricinus communis; Pt, Populus trichocarpa; Md, Malus domestica; Vv, Vitis vinifera; Cs, Cynara scolymus; Tk, Taraxacum kok-saghyz; Ha, Helianthus annuus; St, Solanum tuberosum; Sd, Solanum demissum; Nt, Nicotiana tabacum; Osj, Oryza sativa subsp. japonica; Or, Oryza rufipogon; Bd, Brachypodium distachyon; Ta, Triticum aestivum; Zm, Zea mays; Pv, Panicum virgatum; Sb, Sorghum bicolor; Pta, Pinus taeda; and Pg, Picea glauca. B and C, Expression of an L. japonicus potential AtCASP functional homolog (LjCASP1) in Arabidopsis. The L. japonicus promoter drives expression exclusively in the endodermis (B), and LjCASP1-GFP localizes to the Casparian strip membrane domain (C). Images show confocal sections of a 5-d-old root. Rectangles in C highlight an endodermal cell; co, cortex; en, endodermis; and ep, epidermis. Bars = 10 μm. D, AtCASP1 EL1 and TM4 are aligned to their closest homologs from the Lamiales. Mimulus guttatus (Mg) and Striga asiatica (Sa) present an AtCASP homolog potentially nonfunctional due to a premature stop codon (asterisks) in TM4. The Utricularia gibba (Ug) closest AtCASP homolog does not show conservation in the EL1 signature. Striga hermontica (Sh), Triphysaria pusilla (Tp), and Mimulus guttatus encode for potential functional AtCASP homologs. See also Supplemental Table S5. [See online article for color version of this figure.]