Figure 7. Model for two mammalian MOF complexes in transcription activation.
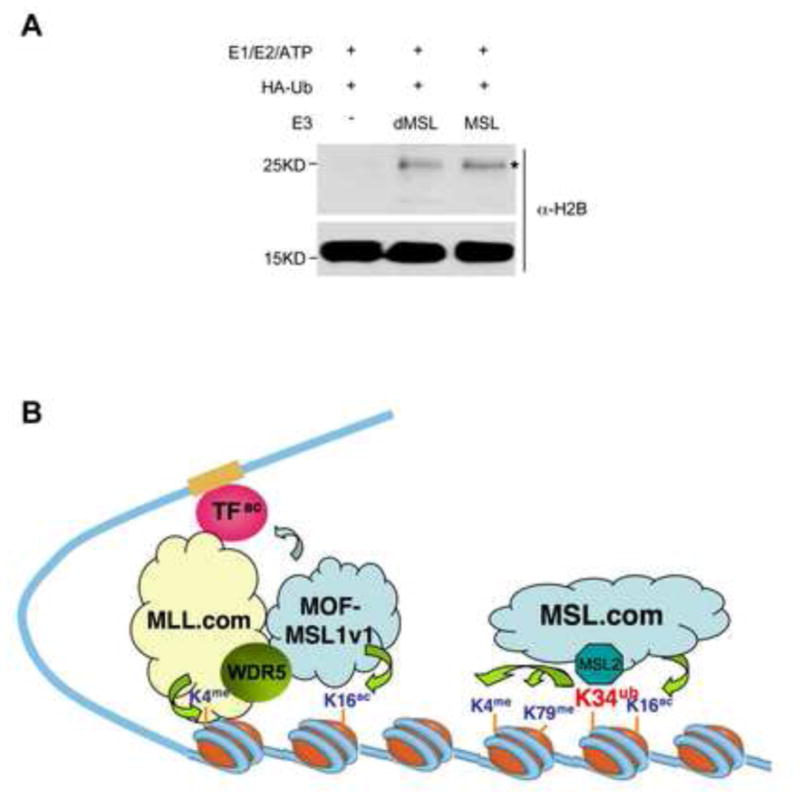
(A) In vitro ub assay for MSL1/2 and the Drosophila dMSL1/2 heterodimer as indicated on top. HeLa nucleosomes were used as the substrate. Histone ubiquitylation were detected by anti-HA antibody and expected ubH2B band is marked with *. Immunoblot for H2B was used as the loading control. (B) Model for the functions of two MOF complexes in transcription regulation. The MOF-MSL1v1 complex, which acetylates H4 and non-histone substrates, is recruited to target genes in coordination with MLL to facilitate transcription initiation. In contrast, the MOF-MSL complex functions to promote both H4 K16ac and H2B K34ub. H2B K34ub, in turn, promotes H2B K120ub, H3 K4me3 and K79me2 to facilitate transcription elongation.
