Figure 2.
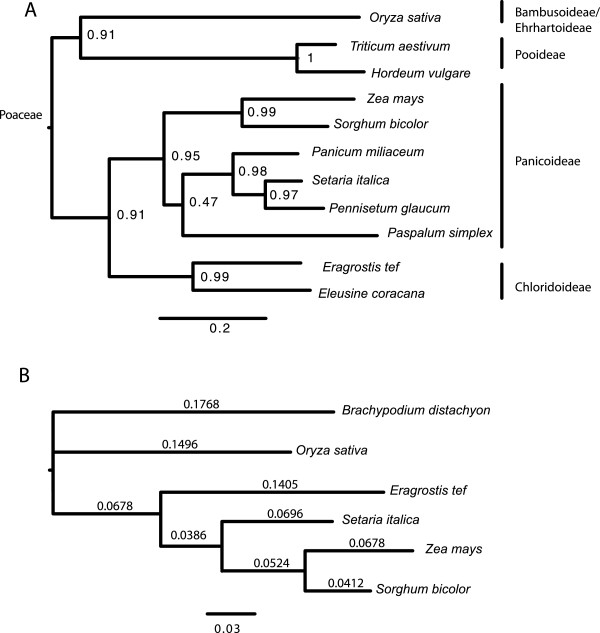
Phylogenetic tree for selected cereals from the grass (Poaceae) family including tef ( Eragrostis tef ). A) Partial sequences of the WAXY gene from barley (Hordeum vulgare, X07931), bread wheat (Triticum aestivum, KF861808), finger millet (Eleusine coracana, AY508652), foxtail millet (Setaria italica, AB089143), maize (Zea mays, EU041692), Paspalum simplex (AF318770), pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum, AF488414), proso millet (Panicum miliaceum, GU199268), rice (Oryza sativa, FJ235770.1), sorghum (Sorghum bicolor, EF089839), and tef (Eragrostis tef, AY136939) were obtained from the NCBI database. The maximum likelihood tree was inferred using PhyML and the default model of HKY85 + G. The scale bar reflects evolutionary distance, measured in units of substitution per nucleotide site. Branch support was inferred using the Shimodaira–Hasegawa-like (SH) aLRT provided by PhyML. B) Phylogenetic Tree of the Complete Grass Genomes. Protein supergenes with an aligned length of 260398 amino acids and constructed from orthologous sequences were used to infer a maximum-likelihood tree using PhyML with the WAG substitution matrix and a gamma model with four classes and an alpha parameter value estimated to be 0.489. Branch lengths reflect the estimated number of amino acid substitutions per site. ML bootstrap values were all 100%.
