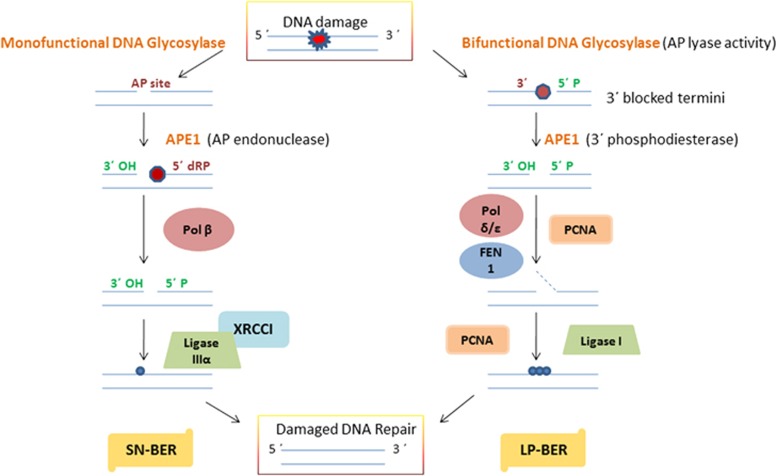
Figure 3.
A schematic representation of the mechanism of the short-patch (SN-BER) and long-patch (LP-BER) sub-pathways of base excision repair (BER) in mammalian cells. apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1)/redox effector factor-1 (Ref-1) functions as an AP endonuclease in SN-BER, initiated by monofunctional DNA glycosylase (DG), and as a 3′phosphodiesterase in LP-BER, initiated by bifunctional DG. Pol β, X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 (XRCC1) and ligase III are required for SN-BER to conduct SN repair, whereas proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), Pol δ/ɛ, flap endonuclease 1 (FEN-1) and ligase I are required for LP-BER to conduct multinucleotide repair in mammalian cells.