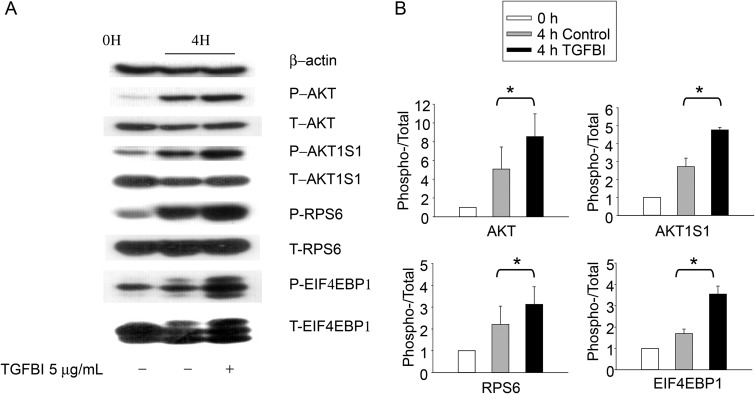
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of molecules putatively involved in TGFBI signaling according to immunoblotting. WT islets were either lysed directly or cultured for 4 h in presence of TGFBI (5 µg/ml) in F-12K serum-free medium and then lysed, as indicated. Lysates were analyzed for phospho-AKT (P-AKT; Ser473), total AKT (T-AKT), phospho-AKT1S1 (P-AKT1S1; Thr246), total AKT1S1 (T-AKT1S1), phospho-RPS6 (P-RPS6; Ser235/236), total RPS6 (T-S6), phospho-EIF4EBP1(P-EIF4EBP1; Thr37/46), and total EIF4EBP1 (T-EIF4EBP1). Beta-actin was included as an additional loading control. The experiments were conducted three times in total, and data from a representative experiment are reported. All blotting in (A) were derived from 1 SDS–PAGE run and one membrane. The data from all three experiments were analyzed by densitometry, and the ratios of signal strength of phosphoproteins versus that of total proteins were illustrated in bar graphs in (B). The differences between TGFBI-treated verses the controls are significant (*P < 0.05, paired Student's t test).