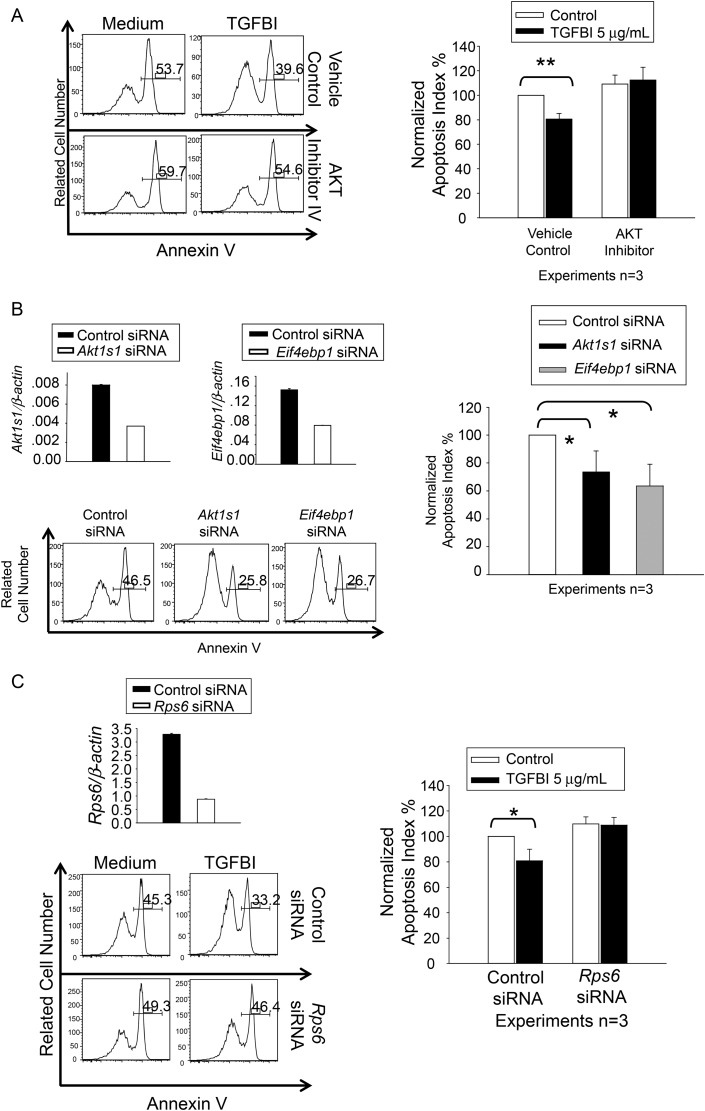
Figure 6.
Islet survival upon modulation of AKT, AKT1S1, RPS6 and EIF4EBP1 activity and expression. Three independent experiments were conducted in (A), (B) and (C), and histograms of a representative experiment are presented, with percentages of annexin V-positive cells. (A) AKT inhibitor IV revokes the beneficial effect of TGFBI on islet survival. WT islets were cultured in F-12K serum-free medium for 72 h in presence and absence of human recombinant TGFBI (5 µg/ml) and AKT inhibitor IV (1 µM), as indicated. Islet cell apoptosis was measured according to annexin V staining, followed by flow cytometry. (B) AKT1S1 and EIF4EBP1 siRNA transfection reduces islet apoptosis. WT islets were transfected with siRNAs targeting AKT1S1 or EIF4EBP1, or with control siRNA. They were cultured in F-12K serum-free medium for 72 h. AKT1S1 and EIF4EBP1 mRNA knockdown was confirmed by RT–qPCR (upper row), with expression as ratios (means ± SD) of targeting gene signals versus β-actin signals. Islet cell apoptosis was measured by annexin V staining, followed by flow cytometry. (C) RPS6 siRNA transfection revokes the beneficial effect of TGFBI on islet survival. WT islets were transfected with siRNAs targeting RPS6, or with control siRNA. They were cultured in F-12K serum-free medium for 72 h in absence or presence of TGFBI (5 µg/ml), as indicated. Rps6 mRNA knockdown was confirmed by RT–qPCR (upper row), with expression as ratios (means ± SD) of targeting gene signals versus β-actin signals. Islet cell apoptosis was measured by annexin V staining, followed by flow cytometry. The experiments in (A), (B), and (C) were conducted a total of three times, and the data are summarized in bar graphs at the right of each panel. Differences with statistical significance (paired Student's t tests) are indicated with asterisks (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).