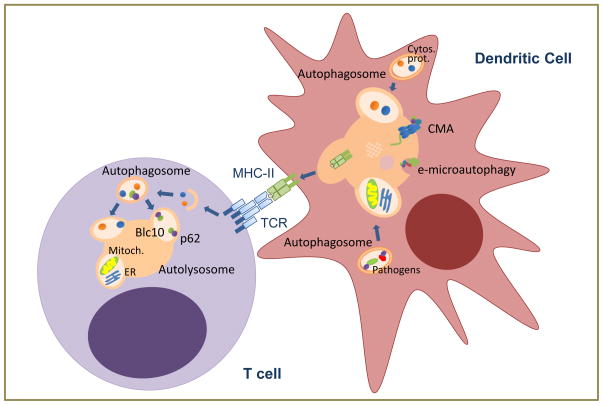
Figure 2. Autophagic functions in adaptive immunity.
In dendritic cells, cytosolic proteins or those derived from intracellular pathogens can be delivered to be loaded into MHC-II through macroautophagy, CMA or endosomal microautophagy (e-microautophagy) to activate T cells. Whereas basal macroautophagy in T cells regulates organelle homeostasis (including mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum), activation-induced macroautophagy in response to TCR engagement degrades cytosolic components to respond to increased metabolic demand and to modulate specific signaling pathways.