Figure 3.
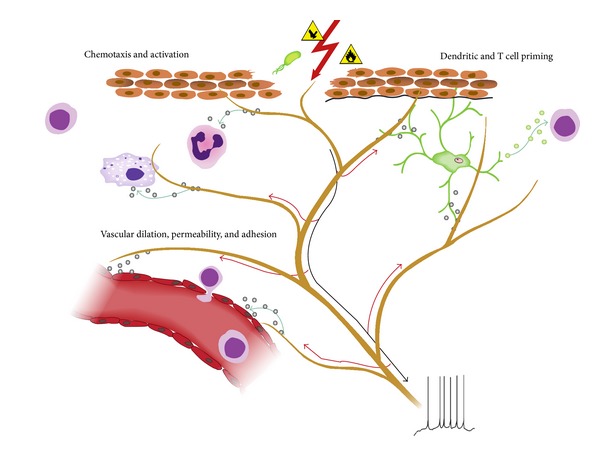
Neurogenic inflammation. Neuronal factors released from nociceptor sensory neurons directly drive leukocyte chemotaxis, vascular hemodynamics, and the immune response. When noxious stimuli activate afferent signals in sensory nerves, antidromic axon reflexes are generated that induce the release of neuropeptides at the peripheral terminals of the neurons. These molecular mediators have several inflammatory actions: (1) chemotaxis and activation of neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes to the site of injury and degranulation of mast cells. (2) Signaling to vascular endothelial cells to increase blood flow, vascular leakage, and edema. This also allows easier recruitment of inflammatory leukocytes. (3) Priming of dendritic cells to drive subsequent T helper cell differentiation into Th2 or Th17 subtypes. Reproduced from Chiu et al., 2012, with permission [63].
