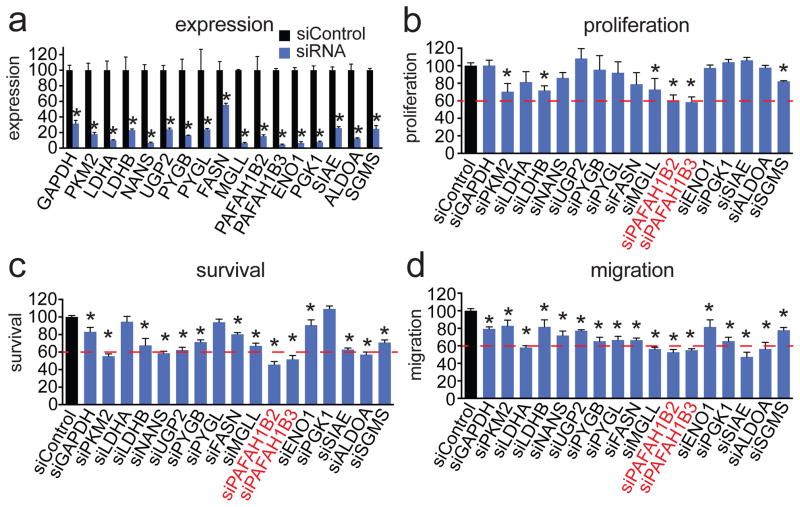
Figure 2. Screening for nodal metabolic enzymes in breast cancer.
(a) We transiently knocked down the expression of representative metabolic enzymes in the pathways that we identified as consistently dysregulated in the breast cancer progression model with siRNA in MII TAZ S89A cells. Knockdowns were confirmed by qPCR 48 h after siRNA transfection (b–d). We screened for enzymes that, when inactivated, impaired various aspects of cancer pathogenicity including cellular proliferation (b), serum-free cell survival (c), and cell migration (d) in MII TAZ S89A cells. Cells were transfected with siRNA for 48 h before seeding into phenotypic experiments. Proliferation and cell survival were assessed 48 h after seeding cells by the WST1 cell viability assay. Migration was assessed by counting the number of cells migrated through Transwell chambers over 24 h. Data in bar graphs are presented as mean ± sem; n = 3–5/group normalized to siControl. Significance is presented as *p < 0.05 compared to siControl MII TAZ S89A control cells.