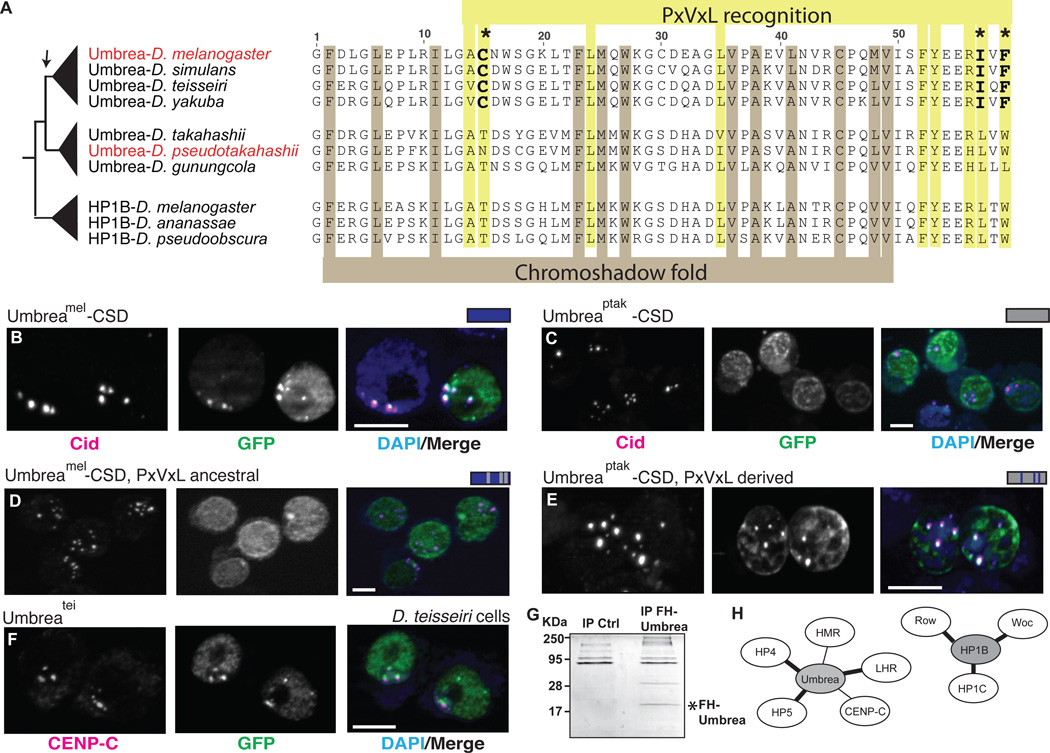
Fig. 3. Chromoshadow changes led to Umbrea centromere localization via altered protein-protein interactions.
(A) An amino acid alignment of HP1B and Umbrea CSDs reveals conservation of fold-defining residues but divergence in PxVxL-recognition residues. In particular, 3 changes (bold) are predicted to affect the binding specificity of Umbrea CSD. (B) GFP-tagged Umbreamel CSD (green) colocalizes with Cid (magenta) at centromeres in D. melanogaster Kc cells (bar = 5 microns, colocalization appears white). (C) However, GFP-tagged Umbreaptak CSD does not localize to centromeres. (D) Reversion of Umbreamel PxVxL-recognition residues (C-I-F) to ancestral states (T-L-W) causes delocalization from centromeres. (E) In contrast, introducing PxVxL-recognition residues (C-I-F) is sufficient to localize Umbreaptak CSD to centromeres (compare to Fig. 3C). (F) Umbreatei colocalizes with centromeric protein CENP-C in D. teissieri cells. (G) Immunoprecipitation of Flag-HA-tagged Umbrea pulls down protein complexes in S2 cells. (H) Analysis of these complexes reveals that Umbrea and HP1B have mutually exclusive protein-protein interactions. Umbrea interacts with centromere and heterochromatin proteins (Table S2, bold lines indicate confirmation of previously reported interactions(9, 17)), but not with the primary targets of HP1B(18).