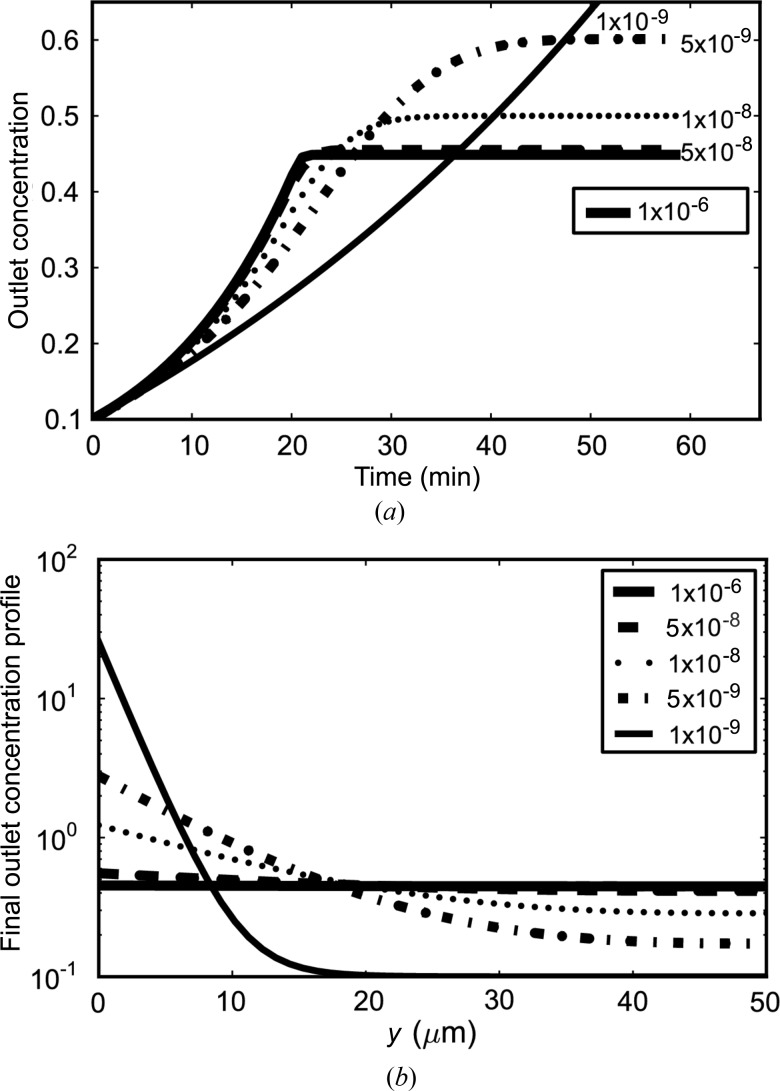
Figure 7.
Theoretical chip performance with various types of proteins. Number labels are diffusion constants in cm2 s−1. (a) Time to reach steady state is 20 min (effect of dead volume not shown) for fast-diffusing proteins. Slow proteins and aggregates take more than 30 min but are more concentrated when they reach the outlet. (b) Steady-state concentration gradient at outlet. For proteins faster than a certain threshold (8.5 × 10−8 cm2 s−1), the profile is flat and the final concentration and equilibration time are independent of diffusion. Slow proteins or aggregates are diffusion-limited and concentrate in the slow-moving flow near the membrane surface. As such, they take much longer to elute but ultimately reach a higher concentration.