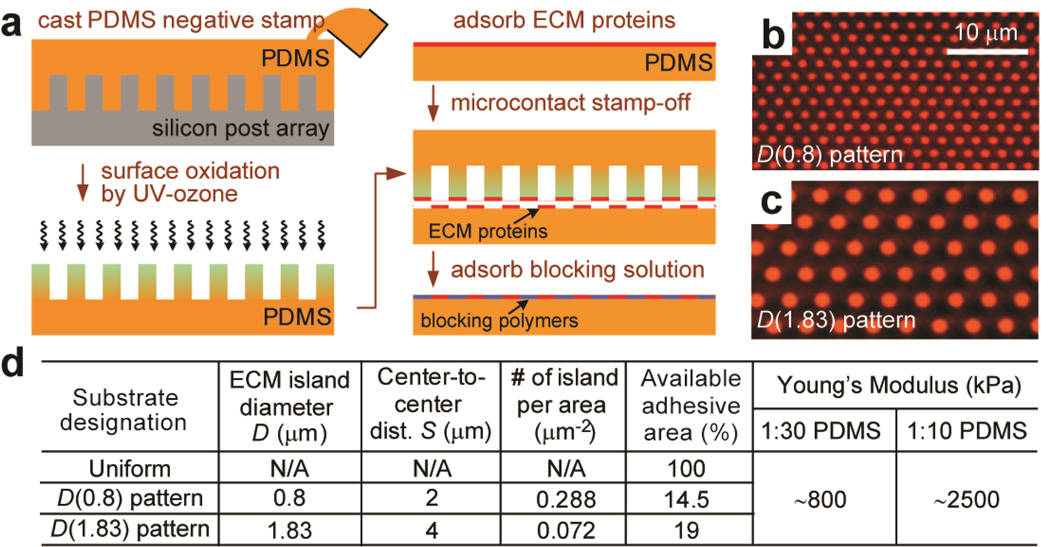
Figure 2.
Flat PDMS substrates patterned with adhesive ECM islands using microcontact stamp-off. (a) Schematic of microcontact stamp-off to pattern flat PDMS surfaces with adhesive ECM islands. (b&c) Fluorescence images of flat PDMS surfaces coated with arrays of hexagonally arranged circular ECM islands using microcontact stamp-off (b: D=0.8 µm, S=2 µm; c: D=1.83 µm, S=4 µm). Bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugated with Alexa Fluor-555 was used for visualization of patterned proteins. Note the lack of fluorescence signal outside of the patterned circles, indicting complete protein removal using microcontact stamp-off. (d) Table summarizing flat PDMS substrates coated with different ECM patterns as controls for the comparative studies. ‘Uniform’ PDMS surfaces were coated uniformly with ECM proteins by natural adsorption. ‘D(0.8) pattern’ PDMS substrates were coated with circular ECM islands with D=0.8 µm and S=2 µm, while ‘D(1.83) pattern’ PDMS substrates were coated with circular ECM islands with D=1.83 µm and S=4 µm. PDMS with different curing agent:base ratios (1:30 and 1:10; w/w) were used to regulate substrate rigidity.