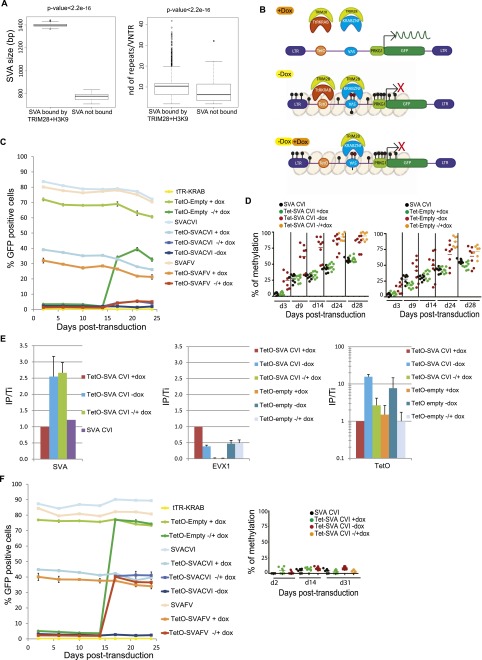
Figure 5.
Interdependence between TRIM28-mediated SVA recruitment and DNA methylation. (A) TRIM28-bound SVAs are larger (left) and contain significantly more repeat units (right) than their TRIM28-devoid counterparts (10 versus 7 on average, P-value: Wilcoxon nonparametric test). (B) Working model to probe the DNA methylation dependence of TRIM28 recruitment to SVAs. In the presence of dox (top), tTR-KRAB is sequestered away from its TetO DNA target, and no repression occurs. In the presence of dox (middle), tTR-KRAB-induced heterochromatin formation (pink balls) leads to DNA methylation of adjacent sequences (black circles), including the SVA insert, which is then recognized by a putative SVA-specific KRAB-ZFP, and of the PRKG1 promoter, which is silenced. When dox is added (bottom), tTR-KRAB is removed, but the SVA-bound KRAB-ZFP maintains transcriptional repression. (C) tTR-KRAB-expressing hES cells were transduced in duplicate with lentivectors containing only TetO (TetO-Empty), only SVA (SVACVI or SVAFV), or both sequences upstream of a PRKG1-GFP cassette. Cells were maintained off (−Dox), on (+Dox), or 14 d off followed by 14 d on Dox (±Dox), and GFP expression was monitored over time by FACS. Results are representative of three independent experiments with similar results up to 31 d post-transduction. (D) Methylation of the PRKG1 promoter, contained in indicated vectors and conditions detailed in C, was monitored by pyrosequencing. Each dot represents a CpG (n = 8 except in ± conditions where n = 7). (E) TRIM28-specific ChIP-qPCR on chromatin harvested from indicated settings, with primers specific for the vector-contained SVA and TetO motifs or for the cellular EVX1 gene as a negative control. Bars represent mean and SD of two independent experiments (with n = 3 technical replicates). Immunoprecipitates were normalized to the total input (IP/Ti) and enrichment on the positive control ZNF180. (F) SVA-induced repression is de novo DNA methylation-dependent. (Left) Same as in C but in DNMT3A- and DNMT3B-depleted hES cells. The silencing of the PRKG1 promoter is reversible upon dox addition whether or not a SVA sequence is present. (Right) Pyrosequencing demonstrating the absence of de novo DNA methylation on the promoter in DNMT3A/DNMT3B KD cells.