Figure 4. ADAM10 is responsible for the loss of ephrinB2 expression in the absence of flotillin-1.
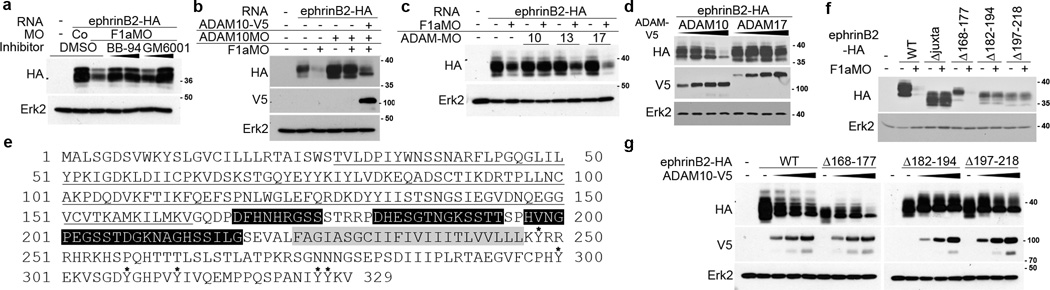
(a) Metalloproteases are responsible for the loss of ephrinB2 expression in the absence of flotillin-1. Western analysis of ephrinB2-HA expression in the presence of CoMO or F1aMO and increasing amounts of the broad-spectrum metalloprotease inhibitors BB-94 and GM6001, as indicated. (b) ADAM10 reduces ephrinB2 expression, but is inhibited by the presence of endogenous flotillin-1. Western analysis of ephrinB2-HA in embryos injected with ADAM10MO and/or F1aMO, and ADAM10-V5 RNA as indicated. Erk2 is used as a loading control. (c) Specific knockdown of ADAM10 rescues ephrinB2 loss in the presence of F1aMO. Western analysis of ephrinB2-HA in the presence of F1aMO alone or with the indicated ADAM MO. Erk2 is used as a loading control. (d) ADAM10 overexpression reduces ephrinB2 expression in a dose-dependent manner. Western analysis of embryos expressing ephrinB2-HA with increasing amounts of ADAM10-V5 or ADAM17-V5. (e) EphrinB2 amino acid sequence. Black line indicates the globular region of the ephrinB2 ectodomain that is known to bind Eph receptors. The black boxes indicate amino acids 168–177, 182–194, and 197–218 in the juxtamembrane region of the ephrinB2 ectodomain, the grey box denotes the transmembrane domain, and the six asterisks indicate the six tyrosine residues in the intracellular domain of ephrinB2. (f) Amino acids 182–214 of ephrinB2 are important for the decrease in ephrinB2 mediated by F1MO. Western analysis of ephrinB2 mutants lacking the indicated amino acids or juxtamembrane domain in the presence or absence of F1aMO. (g) Amino acids 182–214 of ephrinB2 are important for the decrease in ephrinB2 mediated by ADAM10. Western analysis of ephrinB2 mutants lacking the indicated amino acids or juxtamembrane domain in the presence or absence of ADAM10.
