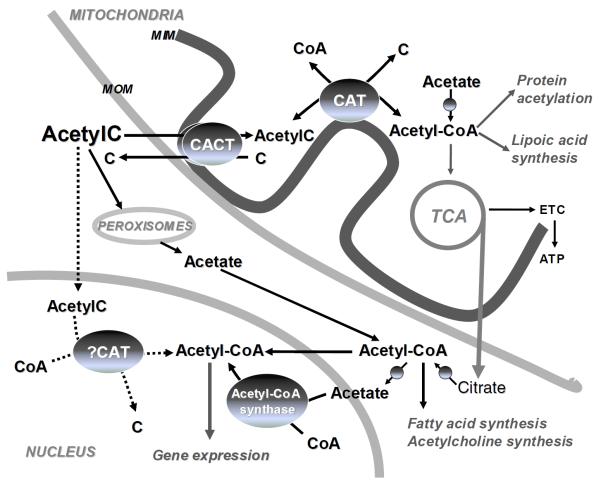
Figure 1. Metabolic fate of acetyl-CoA derived from acetylcarnitine.
The supplemented acetylcarnitine (AcetylC) is transported into the mitochondria via the inner membrane carnitine acylcarnitine transferase (CACT). Acetyl-CoA formed through the mass-action of carnitine acetyltransferase (CAT) or synthesized de novo from acetate becomes available for tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), lipoic acid synthesis, and mitochondrial protein acetylation. Cytosolic acetyl-CoA is derived from transported mitochondrial citrate or peroxisomal acetate. Nuclear acetyl-CoA is either directly imported from the cytosol or synthesized from acetate by acetyl-CoA synthetase or via the potential nuclear CAT using acetylcarnitine. Nuclear acetyl-CoA controls gene expression via acetylation of histone and non-histone proteins.