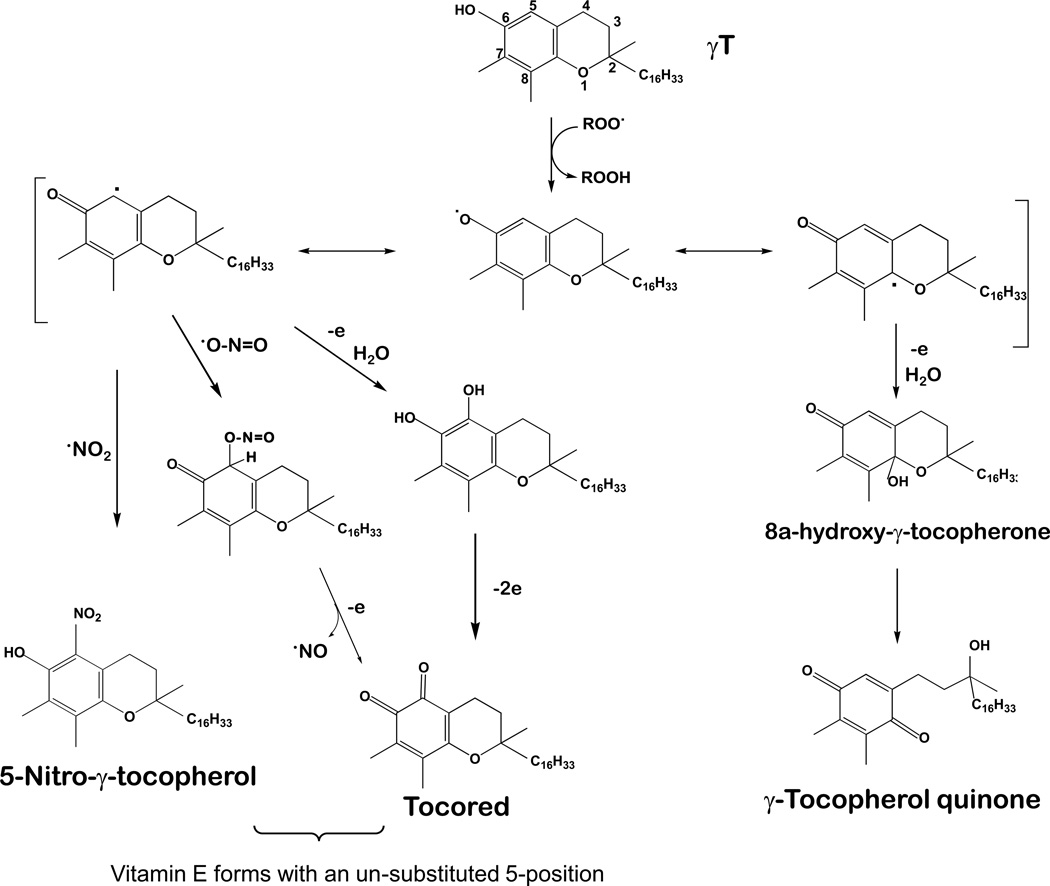
Figure 3. Antioxidant activities of vitamin E forms (representatively shown by γT).
Tocopherols and tocotrienols are potent lipophilic antioxidants by scavenging lipid peroxyl radicals via donating hydrogen from the phenolic group on the chromanol ring. Vitamin E forms with an un-substituted 5-position including γT may trap electrophiles such as NO2 or peroxynitrite to form 5-nitro-γ-tocopherol (5-NγT). This figure is modified based on ref [1].