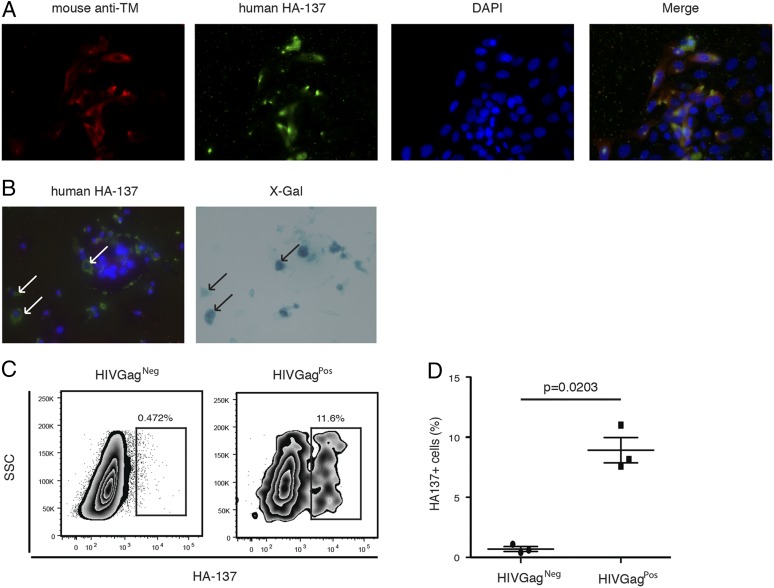
FIGURE 1.
Identification of linear Ab epitopes in HERV-K (HML-2) TM expressed by infected cells. (A and B) Immunofluorescence. Representative images of HERV-K TM surface expression on infected TZMbl cells. Original magnification ×40. The detection of TM protein surface expression was performed by immunofluorescence on in vitro HIV-1LAI–infected TZMbl cells 2 d postinfection. (A) Red: mouse anti–HERV-K (HML-2) TM; green: HA-137; blue: nucleus. (B) Green: HA-137; blue: nucleus (left panel). Blue: X-gal staining (right panel). Arrows represent coexpression of HIV-1 Tat protein (right panel) and HA-137 epitope (left panel). (C) Representative flow cytometry plots depicting HA-137 extracellular binding on infected PBMCs. HA-137 recognition was assessed by measuring the frequency of HA-137Alexa Fluor 488+ cells gated on live HIVGag+ or HIVGag− cells from infected PBMCs. (D) Cumulative data from three independent experiments. The horizontal line represents the median in each group. The p value was derived by the Mann–Whitney T test.