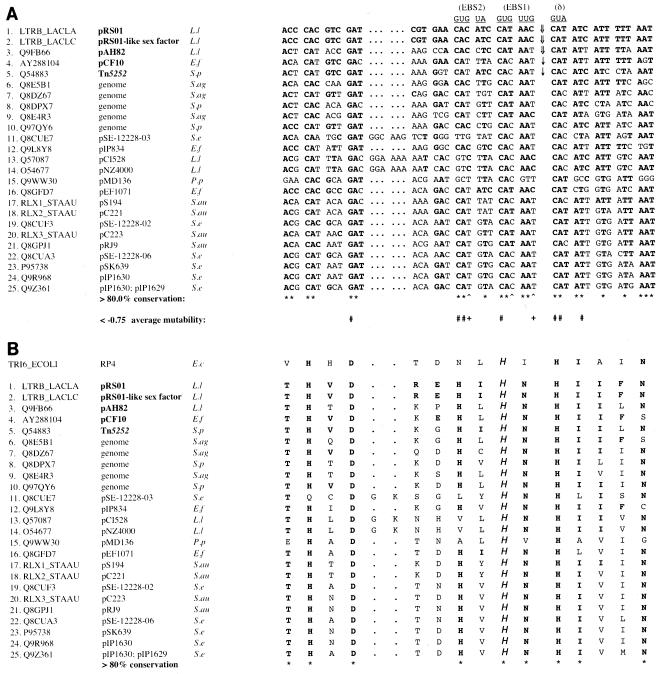
FIG. 1.
The Ll.ltrB target site encodes a highly conserved relaxase domain. Sequence identifiers (except the pcfG GenBank identifier) correspond to those given in the Pfam database (http://pfam.wustl.edu/). Sequences of Q9FB66 and LTRB_LACLC are given according to the updated exon-intron junctions of Dai and Zimmerly (10). Calculations of overall nucleotide and amino acid conservation are based exclusively on sequences listed on the Pfam database. E.f, Enterococcus faecalis; L.l, L. lactis; P.p, Pediococcus pentosaceus; S.ag, Streptococcus agalactiae; S.au, Staphylococcus aureus; S.e, Staphylococcus epidermidis; S.p, Streptococcus pneumoniae. (A) Nucleotide sequences homologous to the ltrB insertion site (positions −30 to +15 with respect to the Ll.ltrB insertion). Nucleotides of Ll.ltrB intron RNA that base pair with ltrB during homing are shown above the alignment. Identities with ltrB are indicated with boldface type. Wide arrows (⇓) indicate previously identified Ll.ltrB family intron insertion sites in nature, while narrow arrows (↓) indicate Ll.ltrB insertion sites determined experimentally in this work. Asterisks below the alignment indicate >80% conservation of ltrB-type nucleotides, while carets indicate combined conservation of >80% of C and T at positions that are thought to base pair with specific G residues in Ll.ltrB RNA. Pound signs (#) indicate average mutability values of less than −0.75 for non-ltrB-type nucleotides, as described in the text. Plus signs represent average mutability values of less than −0.75 for A and G nucleotides at positions where wild-type ltrB residues (C or T) base pair with specific G residues in intron RNA. (B) Predicted relaxase polypeptide sequences encoded by the nucleotide sequences shown in panel A. Putative functional histidine residues are indicated by “H.” Asterisks indicate >80% conservation of LtrB-type amino acids. Homologous sequence from the TraI relaxase protein, including its functional histidine, is shown above the alignments.