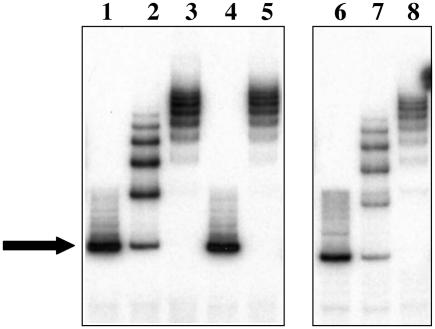
FIG. 2.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay indicates that TcaR binds to the ica promoter. Lanes 1 to 5 show mobility shift analysis of the probe representing the wild-type strain MN8 ica promoter. Additions to this probe were as follows: lane 1, nothing (free probe only); lane 2, 5 ng (14 nM) of purified recombinant TcaR; lane 3, 25 ng (70 nM) of TcaR; lane 4, a 100-fold excess of specific competitor (unlabeled wild-type probe) and 25 ng (70 nM) of TcaR; and lane 5, 100-fold excess nonspecific competitor (198 bp sequence from icaA) and 25 ng (70 nM) of TcaR. Lanes 6 to 8 show mobility shift analyses of the probe representing the ica promoter of the mucoid strain MN8m (MUC). Additions to this probe were as follows: lane 6, nothing (free probe only); lane 7, 5 ng (14 nM) of TcaR; and lane 8, 25 ng (70 nM) of TcaR. The solid arrow indicates the free probe. TcaR induced a number of shifts in both the wild-type and mutant probes.