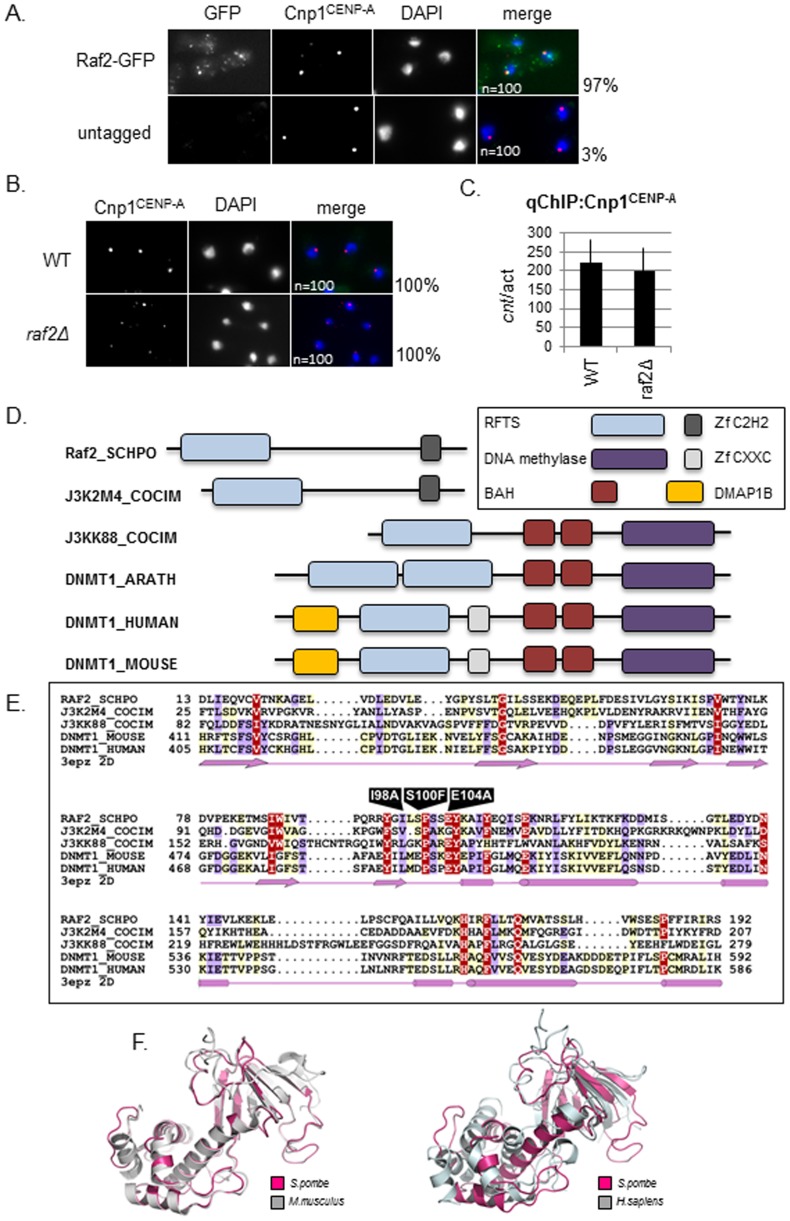
Figure 1. Raf2 is an RFTS domain protein and localises to the nucleus.
A. Analysis of Raf2 localisation in wildtype cells by immunofluorescence. Raf2 localises predominantly to the nucleus and colocalises with Cnp1 at centromeres (numbers indicate % cells displaying colocalisation n = 100). Representative images show staining of fixed cells for Raf2-GFP (green), Cnp1 (red) and DNA (DAPI-blue). B. Analysis of Cnp1 localisation in raf2Δ cells. Cnp1 remains localised in cells lacking Raf2 (numbers indicate % cells displaying localisation n = 100). Representative images show staining of fixed cells for Cnp1(red) and DNA (DAPI-blue). C. ChIP analysis of Cnp1 levels in raf2Δ cells. Cnp1 remains associated with the central core domain in cells lacking Raf2. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM). D. Schematic diagram showing the domain architectures of Raf2 and DNMT1 families. Sequences are named according to their UniProt names. Full species names are: RAF2_SCHPO, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; J3K2M4_COCIM, Coccidioides immitis; J3KK88_COCIM, Coccidioides immitis; DNMT1_ARATH, Arabidopsis thaliana; DNMT1_HUMAN, Homo sapiens, DNMT1_MOUSE, Mus musculus. E. Multiple sequence alignment of RFTS domain. The human DNMT1 RFTS domain secondary structure (pdb: 3epz) is shown below. Arrows and cylinders depict sheets and helices respectively. Residues which are subject to mutation are labeled. The amino acid colouring scheme indicates average BLOSUM62 scores (which are correlated with amino acid conservation) for each alignment column: red (greater than 2), violet (between 2 and 1) and light yellow (between 1 and 0.2). Sequences are named according to their UniProt names (for full species names see Figure 1D legend). F. Left: Structural alignment of Raf2 RFTS domain (pink) with murine DNMT1 (grey). Right: Structural alignment of Raf2 RFTS domain with human DNMT1 (grey).