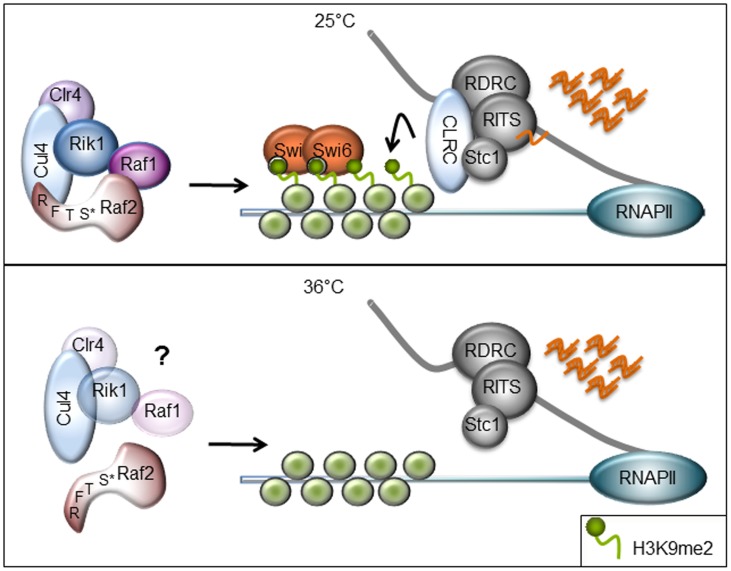
Figure 6. Schematic diagram of heterochromatin defect in Raf2 RFTS mutants.
Cells containing point mutations within the RFTS domain of Raf2 maintain an intact CLRC at 25°C, siRNAs are generated from non-coding RNA transcripts originating from the centromere and chromatin modifications are targeted back to homologous regions. At 36°C, the point mutations cause a conformational change within Raf2 and interfere with its interaction with Cul4. In disrupting CLRC interactions, the Raf2 RFTS mutants cause loss of H3K9 methylation as Clr4 may no longer be targeted to chromatin.