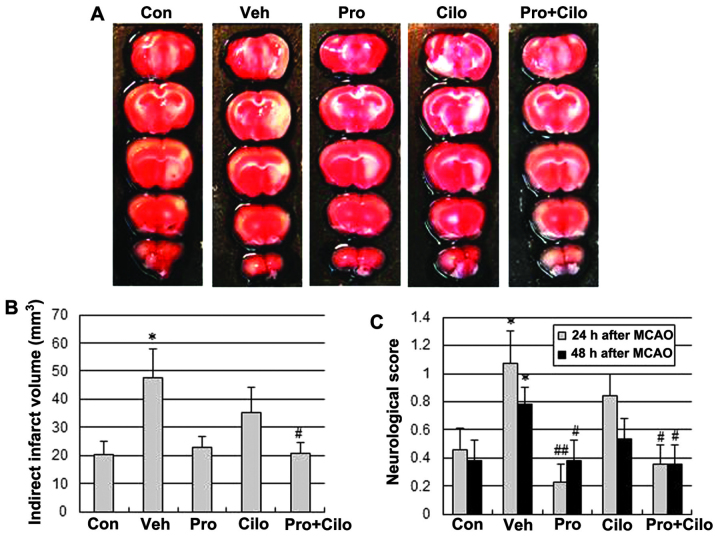
Figure 1.
Effect of probucol plus cilostazol in combination on infarct volume and neurological deficit in cerebral ischemic mice with hypercholesterolemia. (A) Representative images of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC)-stained brains from apolipoprotein E (ApoE) knockout (KO) mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD) with or without 0.3% probucol (Pro), 0.2% cilostazol (Cilo) or 0.3% probucol plus 0.2% cilostazol for 10 weeks. Mice were subjected to 40 min MCA occlusion followed by 48 h reperfusion. White indicates the infarct area. (B) Quantification of infarct volume at 48 h after ischemia (n=10–11). Infarct volume was calculated by integrating the infarct area in 2 mm-thick coronal slices. (C) Neurological deficit was assessed in each mouse at 24 and 48 h after ischemic insult in a blinded manner (n=12–14). Values are the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *P<0.05 vs. age-matched ApoE KO mice without HFD [Con (control)]; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 vs. age- and diet-matched ApoE KO mice [Veh (vehicle)].