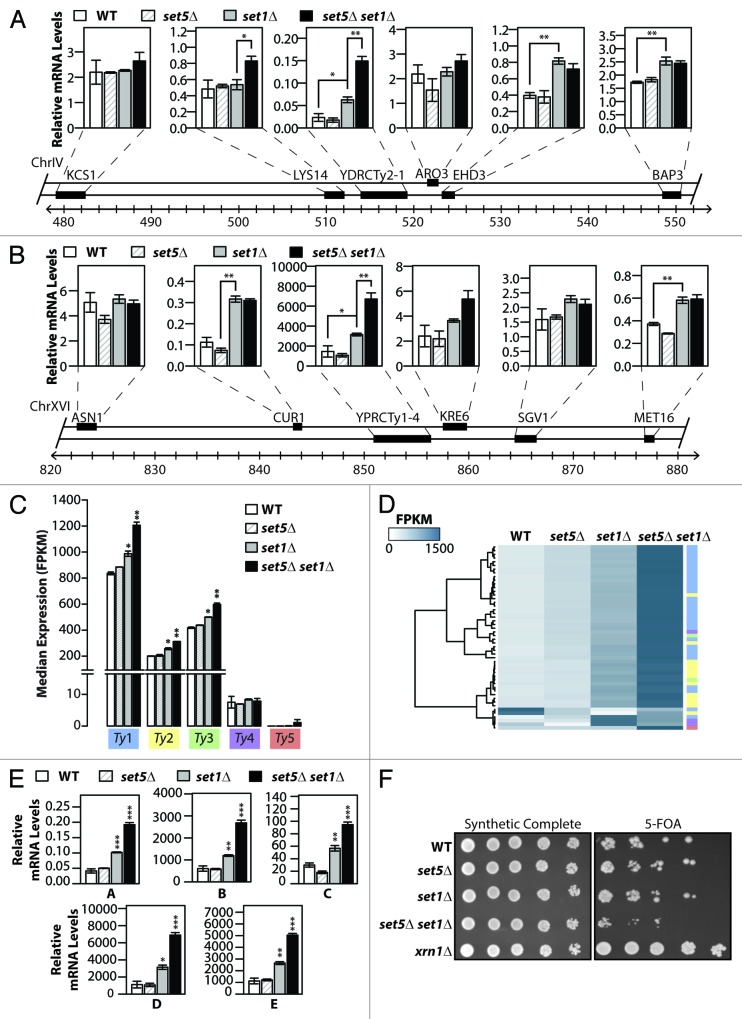
Figure 3. Loss of SET5 and SET1 results in increased transcription of transposable elements. (AandB) Quantitative RT-PCR measurements of mRNA levels of the Ty element YDRCTy2–1 (gene YDR034C-D) and YPRCTy1–4 (genes YPR158C-D and YPR158C-C) and the indicated ORFs located nearby on chromosome IV (A) and chromosome XVI (B) for wild type (WT) and mutant strains. Relative mRNA values were calculated relative to a reference gene, as described in Methods. (C) RNA-Seq median FPKM expression of full-length yeast transposable (Ty) elements grouped by family (color-coded) for wild type (WT) and indicated mutant cells. (D) Hierarchically clustered heatmap of full-length Ty element FPKM expression in indicated strains. Color code on right represents each of the families depicted in (C). (E) qRT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA levels of the indicated Ty elements, calculated relative to the TFC1 reference gene, in WT and mutant cells. Data are represented as mean ± SEM for 3 biological replicates, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (F) set1∆ set5∆ cells show increased expression of a reporter gene fused to the TY1(ML2) promoter. Serial dilutions of yeast containing the Ty1(ML2)::URA3 reporter were spotted on plates with either synthetic complete media or synthetic media supplemented with 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA). Increased URA3 expression results in decreased growth on 5-FOA containing media.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.