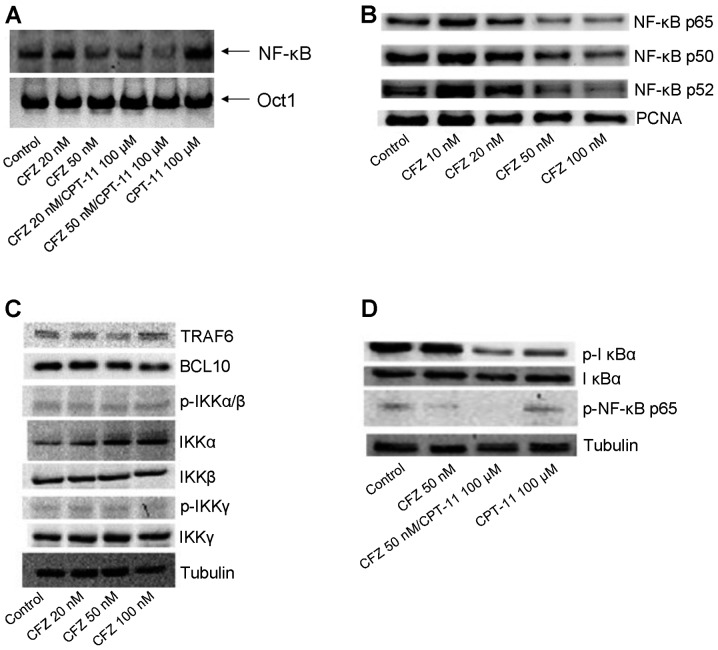
Figure 2.
CFZ alone or combined with CPT-11 inhibits NF-κB activation in SW620 cells. (A) EMSA was used to evaluate the effect of CFZ (20 and 50 nM) ± 100 μM CPT-11 treatment in SW620 cells. Cells were harvested and the nuclear proteins of the cells were extracted and assayed for nuclear translocation of NF-κB at 48 h after of chemotherapy treatment. An Oct1 probe was used as a control for EMSA. (B) The nuclear proteins from SW620 cells were extracted after treatment with 10, 20, 50 and 100 nM of CFZ for 48 h. NF-κB activation was analyzed by western blot analysis. PCNA was used as the internal control for nuclear protein. With increasing concentrations of CFZ, the nuclear protein expression of NF-κB p65, p50 and p52 were gradually reduced. (C) SW620 cells were incubated with 20, 50 and 100 nM of CFZ for 48 h, whole cell lysates were collected and subjected to western blot analysis. IKKα was moderately upregulated but TRAF6, BCL10, p-IKKα/β, IKKβ, p-IKKγ and IKKγ were not changed. (D) After 48 h of chemotherapy treatment, we probed total protein preparations by immunoblot analysis using anti-phospho-IκB, anti-IκB and anti-phospho-NF-κB p65. Tubulin was used as an internal control. CPT-11 (100 μM) combined treatment with CFZ (50 nM) in SW620 cells sharply decrease p-NF-κB p65 activation, and also decrease p-IκB activation but had no effect on the total IκB protein.