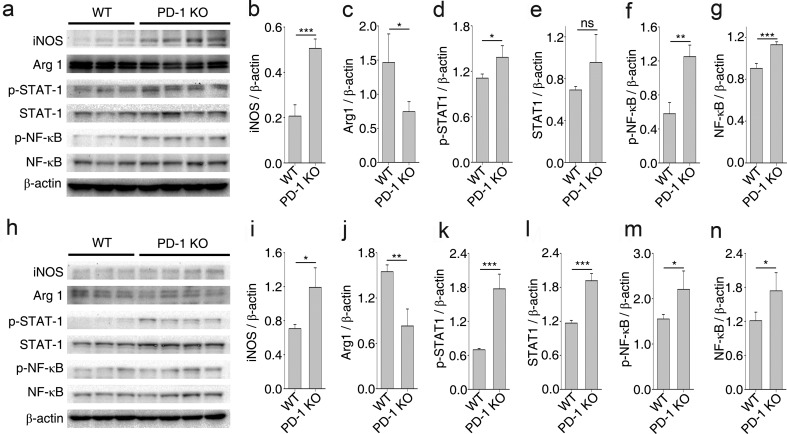
Fig. 6.
Mechanism of programmed death-1 (PD-1) deficiency influences the polarization of macrophages/microglia in vivo after spinal cord injury. (a) Western immunoblot of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), arginase 1 (Arg1), phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription (p-STAT1), signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT1), phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa-B (p-NF-κB), and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) in wild-type (WT) (n = 3) and PD-1-knockout (KO) mice (n = 4) 14 days postinjury (dpi). Densitometric analysis for (b) iNOS, (c) Arg1, (d) p-STAT1, (e) STAT1, (f) p-NF-κB, and (g) NF-κB relative to β-actin. (h) Western immunoblot of iNOS, Arg1, p-STAT1, STAT1, p-NF-κB, and NF-κB in WT mice (n = 3) and PD-1-KO mice (n = 4) 21 dpi. Densitometric analysis for (i) iNOS, (j) Arg1, (k) p-STAT1, (l) STAT1, (m) p-NF-κB, and (n) NF-κB relative to β-actin. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ns = not significant