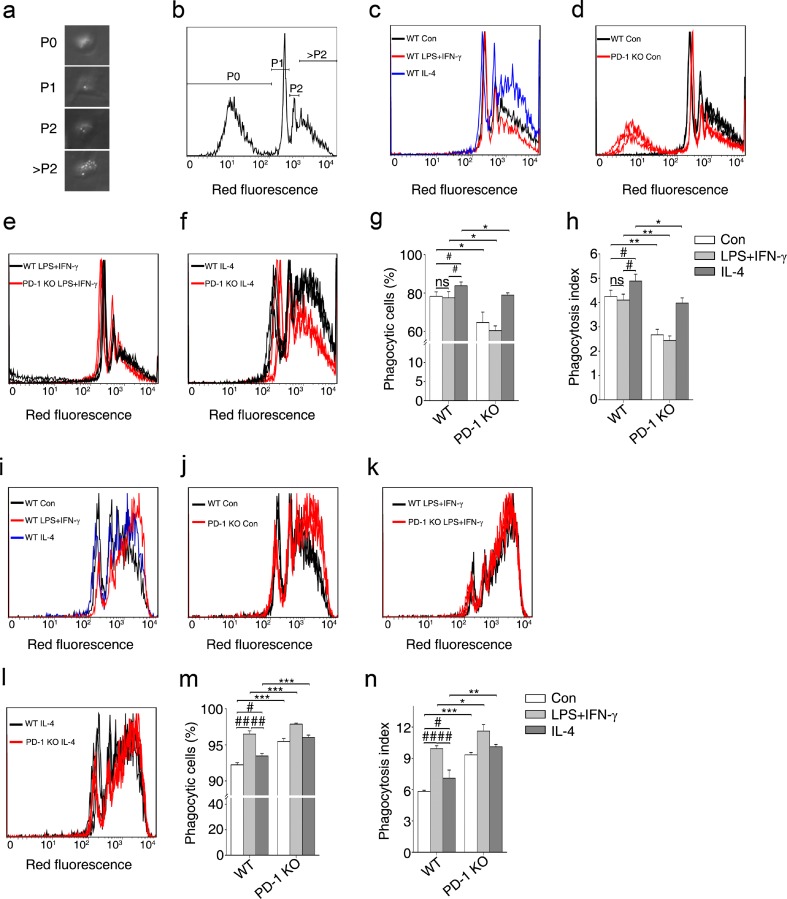
Fig. 7.
A deficiency in programmed death-1 (PD-1) deficiency promotes opposing phagocytic effects in macrophages and microglia. (a) Representative image under light microscopy showing the morphology of macrophages that did not phagocytize any beads (P0), and phagocytized 1 bead (P1), 2 beads (P2), or numerous beads (>P2). (b) Representative diagram showing macrophages with phagocytized beads by flow cytometric analysis. (c) Phagocytosis of wild-type (WT) macrophages under polarized stimulation analyzed by flow cytometry. Phagocytosis of WT and PD-1-knockout (KO) macrophages with (d) no stimulus, (e) lipopolysaccharide (LPS) + interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), or (f) interleukin (IL)-4. (g) The percentage of phagocytic cells calculated in WT and PD-1-KO macrophages. (h) The phagocytosis index calculated in WT and PD-1-KO macrophages. (i) Phagocytosis of WT microglia under polarized stimulation analyzed by flow cytometry. Phagocytosis of WT and PD-1-KO microglia with (j) no stimulus, (k) LPS + IFN-γ, or (l) IL-4. (m) The percentage of phagocytic cells in WT and PD-1-KO microglia. (n) The phagocytosis index calculated for WT and PD-1-KO microglia. n = 3 mice in each group. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 versus WT, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus WT and PD-1-KO. Con = control