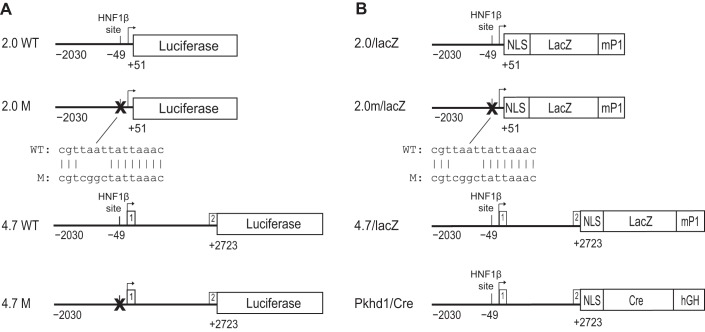
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 (Pkhd1) reporter genes. A: maps of the constructs used for luciferase reporter gene assays in transfected cells. Wild-type (WT) and mutated (M) sequences are shown. Top: 2.0WT is a genomic fragment (horizontal line) containing 2.0 kb of the proximal 5′ flanking sequence, transcription initiation site (arrow), and 51 bp of exon 1 of mouse Pkhd1 linked to a Photinus luciferase reporter gene. A consensus hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)-1β-binding site is located 49 bp upstream from the transcription initiation site. In 2.0M, site-directed mutagenesis was used to mutate the HNF-1β-binding site in the Pkhd1 promoter. Bottom: the alignment of the wild-type and mutated sequences. 4.7WT is a 4.7-kb genomic fragment containing 2.0 kb of the proximal 5′ flanking sequence, exon 1, intron 1, and 30 bp of exon 2 of mouse Pkhd1 linked to a Photinus luciferase reporter gene. 4.7M contains a mutation of the consensus HNF-1β-binding site in the 4.7-kb genomic fragment (X). B: maps of the constructs used to generate transgenic mice. 2.0/lacZ is the genomic fragment containing 2.0 kb of the proximal 5′ flanking sequence and 51 bp of exon 1 of mouse Pkhd1 linked to an Esherichia coli lacZ reporter gene containing a nuclear localization signal (NLS) and an intron and polyadenylation signal from the mouse protamine-1 (mP1) gene. For 2.0m/lacZ, site-directed mutagenesis was used to mutate the HNF-1β-binding site in the Pkhd1 promoter. 4.7/lacZ is a 4.7-kb genomic fragment containing 2.0 kb of the proximal 5′ flanking sequence, exon 1, intron 1, and 30 bp of exon 2 of mouse Pkhd1 linked to the lacZ reporter gene. In Pkhd1/Cre, the 4.7-kb genomic fragment is linked to Cre recombinase containing NLS and a human growth hormone minigene (hGH). Reporter genes are not drawn to scale.