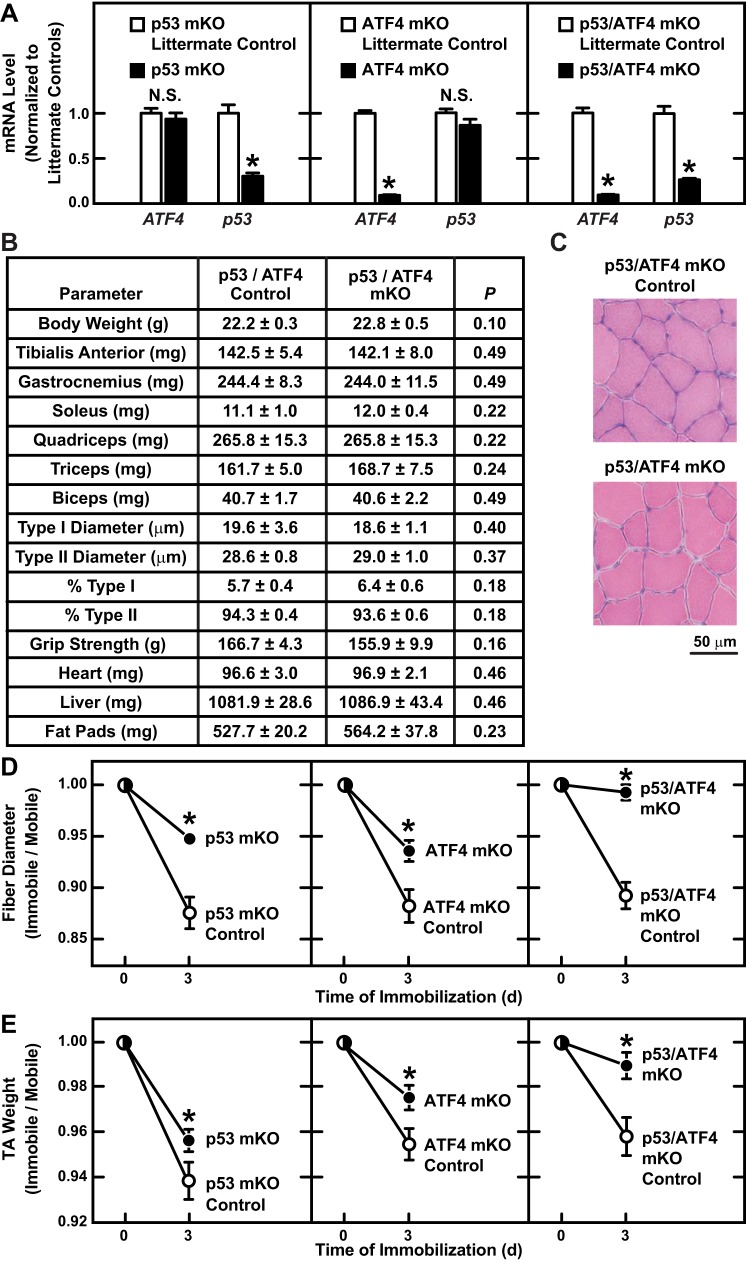
Fig. 6.
Combined loss of p53 and ATF4 prevents immobilization-induced muscle fiber atrophy. p53/ATF4-mKO mice are homozygous for a floxed p53 allele (p53f/f) and a floxed ATF4 allele (ATF4f/f) and possess the MCK-Cre transgene. Control mice for p53/ATF4-mKO were littermates of p53/ATF4-mKO mice that lacked the MCK-Cre transgene. Control mice for p53-mKO were littermates of p53-mKO mice that lacked the MCK-Cre transgene. Control mice for ATF4-mKO were littermates of ATF4-mKO mice that lacked the MCK-Cre transgene. A: mice from the indicated genotypes were subjected to 3 days of hindlimb immobilization, and then immobilized TA muscles were subjected to quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of p53 and ATF4 mRNA levels. Data are means ± SE from ≥6 mice/genotype. P values were determined with unpaired t-tests. *P ≤ 0.05. NS, P ≥ 0.05 (not significant). B: baseline analysis of p53/ATF4-mKO and littermate control mice. Data are means ± SE from 8 mice/genotype. P values were determined with unpaired t-tests. C: representative H & E images from TA muscles of p53/ATF4-mKO and littermate control mice under basal conditions. D and E: bilateral TA muscles were collected from the indicated genotypes before and after 3 days of unilateral hindlimb immobilization. In each mouse, values from the immobile muscle were normalized to values from the mobile muscle. D: muscle fiber size. Data are means ± SE from ≥4 mice/time point (≥250 fibers/muscle measured). Some error bars are too small to see. E: muscle weights. Data are means ± SE from ≥10 mice/time point. Some error bars are too small to see. D and E: at each time point, P values were determined by comparing values from knockout mice to values from their corresponding littermate control mice with an unpaired t-test (*P ≤ 0.05).