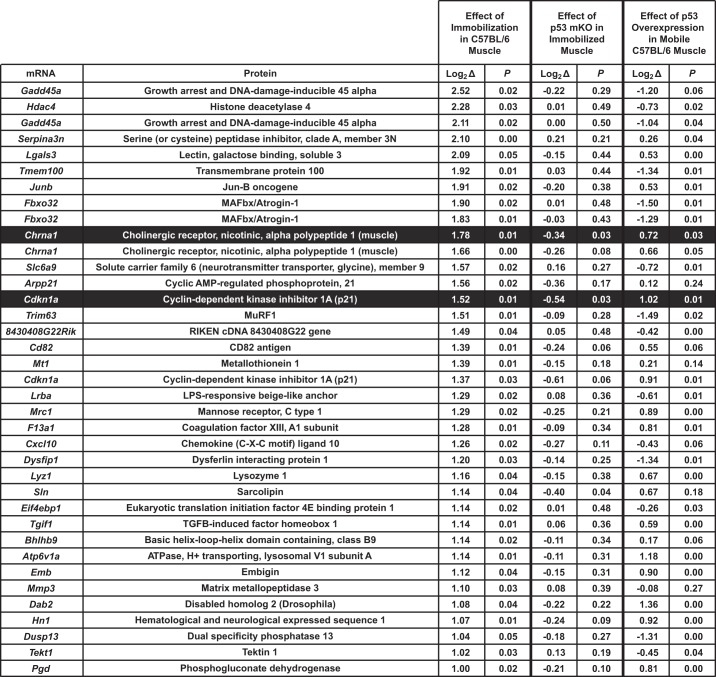
Fig. 8.
Skeletal muscle mRNA transcripts that are ≥2-fold induced by immobilization and the effects of p53 overexpression and p53 gene deletion on those transcripts. C57BL/6 mice were subjected to 3 days of unilateral hindlimb immobilization, and then mRNA levels in bilateral TA muscles were analyzed with Mouse Ref-8 version 2.0 BeadChip arrays. In each mouse, mRNA levels in the immobilized TA were normalized to mRNA levels in the contralateral (mobile) TA, and P values were determined with paired t-tests (n = 4 arrays/condition). Statistical significance was arbitrarily defined as P ≤ 0.05. All mRNAs that were increased ≥2-fold by hindlimb immobilization (33 mRNAs represented by 37 probes) are shown. To determine the effects of p53 gene deletion on these mRNAs, p53-mKO mice and littermate control mice were subjected to 3 days of hindlimb immobilization, and then immobilized TA muscles were harvested and analyzed with Mouse Ref-8 version 2.0 BeadChip arrays. mRNA levels in immobilized p53-mKO muscles were normalized to mRNA levels in immobilized control muscles, and P values were determined with unpaired t-tests (n = 3 arrays/condition). To determine the effects of p53 overexpression on these mRNAs, 1 TA muscle in C57BL/6 mice was transfected with 20 μg of p-wt-p53, and the contralateral TA was transfected with 20 μg of empty plasmid (pcDNA3). Three days later, bilateral TAs were harvested and analyzed with Mouse Ref-8 version 2.0 BeadChip arrays. mRNA levels in muscles transfected with p53 plasmid were normalized to mRNA levels in muscles transfected with control plasmid, and P values were determined with paired t-tests (n = 4 arrays/condition). Shading indicates mRNAs that were ≥2-fold increased by immobilization, reduced by loss of p53, and increased by p53 overexpression.