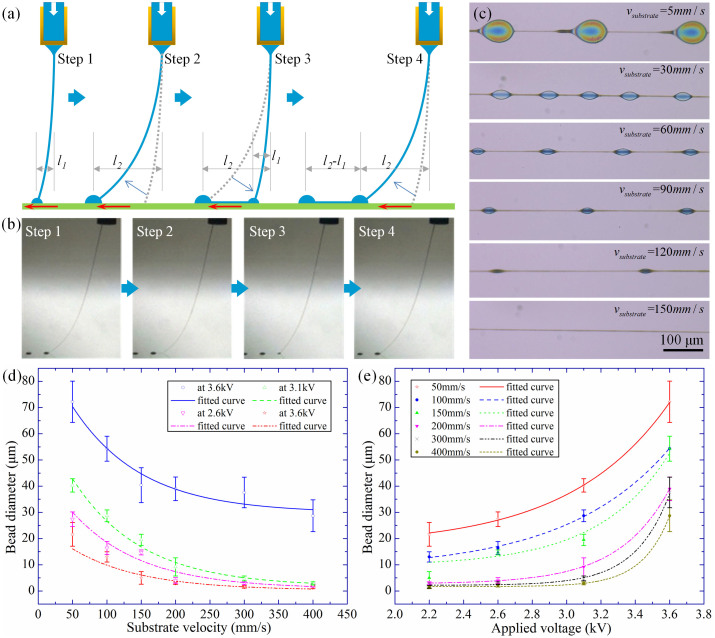
Figure 6.
The leap direct-writing technique: (a) the schematic diagram of leap direct-writing: the ink first accumulates at contact point and then gets stretched by mechanical drawing force. At a critical distance, the ink leaps to the next contact point, and gets stretched again; (b) the leap direct-writing is captured by high-speed camera, similar with (a); and (c) different structures are deposited in the condition of applied voltage (1 kV), nozzle-to-substrate distance (2 mm), flow rate (50 nl/min). (d) and (e) show the effects of substrate speed and voltage on bead diameter. (d) The color lines are fitting curves at different applied voltage. The error bars present the standard deviation to the average values of 10 measurement results. (e) The color lines are fitting curves at different substrate speed. Supply rate, nozzle-to-substrate distance and nozzle diameter are 1200 nl/min, 7.5 mm and 145 μm, respectively.