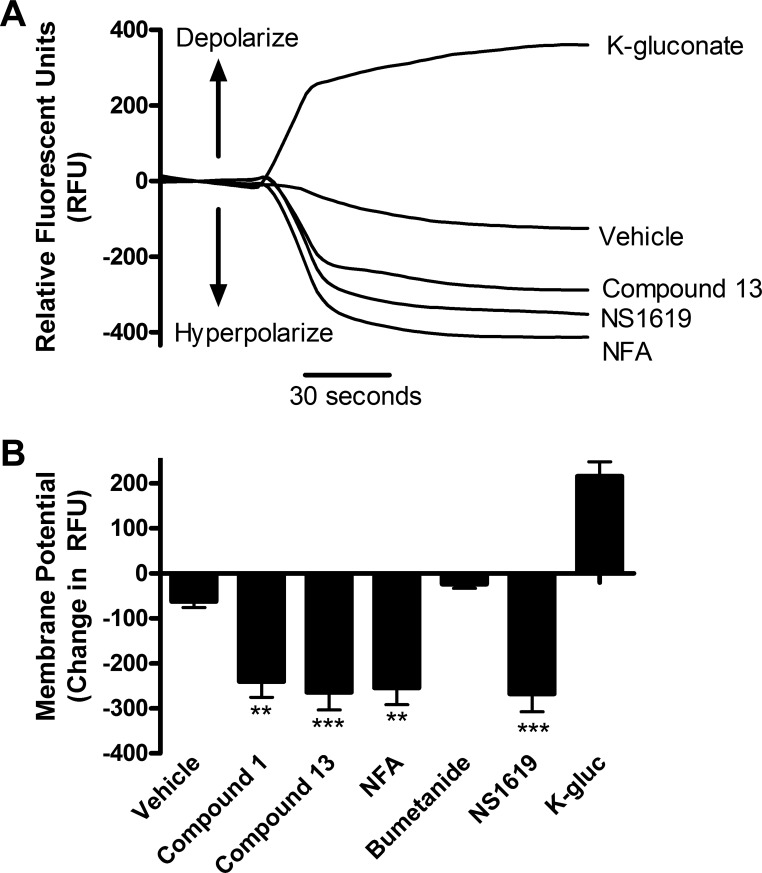
Fig. 7.
Chloride channel blockers hyperpolarize human airway smooth muscle cells. A: representative tracing of continuous fluorescence recordings with fluorescent imaging plate reader (FLIPR) dye. Potassium gluconate (K-gluc) depolarizes, whereas NS1619 (K+-channel opener), compound 13, and NFA hyperpolarize human ASM cells. Potassium gluconate and NS1619 were used as controls as they are known to depolarize and hyperpolarize, respectively. B: change in relative fluorescent units (RFU) with chloride channel blockers. The 100 μM compound 1 (−240.3 ± 35), compound 13 (−264.2 ± 40), and NFA (−254.7 ± 37) all caused a decrease in membrane potential, whereas 10 μM bumetanide did not cause a significant change. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with vehicle; n = 12.