Fig. 1.
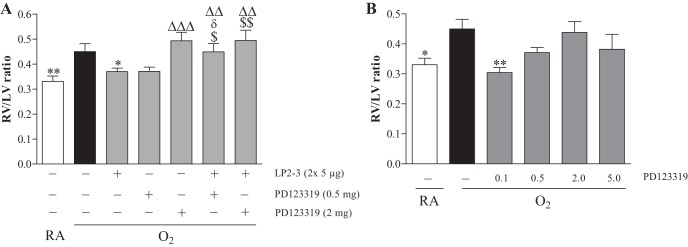
Effect of PD123319 (0.5 and 2 mg·kg−1·day−1) on angiotensin receptor type 2 (AT2) agonist (LP2–3: 5 μg/kg twice a day)-induced prevention of hyperoxia-induced right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) in newborn rat pups on day 10 after birth by morphometry in paraffin sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin and depicted as right ventricle (RV)/left ventricle (LV) wall thickness ratio (N = 6; A). Pilot experiment to find the optimal dose of PD123319 for treatment of experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) by determining RVH depicted as RV/LV wall thickness ratio on day 10 after birth of rat pups (N = 10; B). Rat pups were exposed to room air (RA) and injected daily with saline (open bars) and of rat pups exposed to hyperoxia (O2) and injected daily with saline (solid bars) or PD123319: 0.1, 0.5, 2, and 5 mg·kg−1·day−1 and/or LP2–3 (shaded bars). Data are expressed as means ± SE. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. own age-matched O2-exposed controls. ΔΔP < 0.05 and ΔΔΔP < 0.001 vs. RA controls. $P < 0.05 and $$P < 0.01 vs. AT2 agonist-treated O2 pups. δP < 0.05 vs. PD123319 (0.5 mg·kg−1·day−1).
