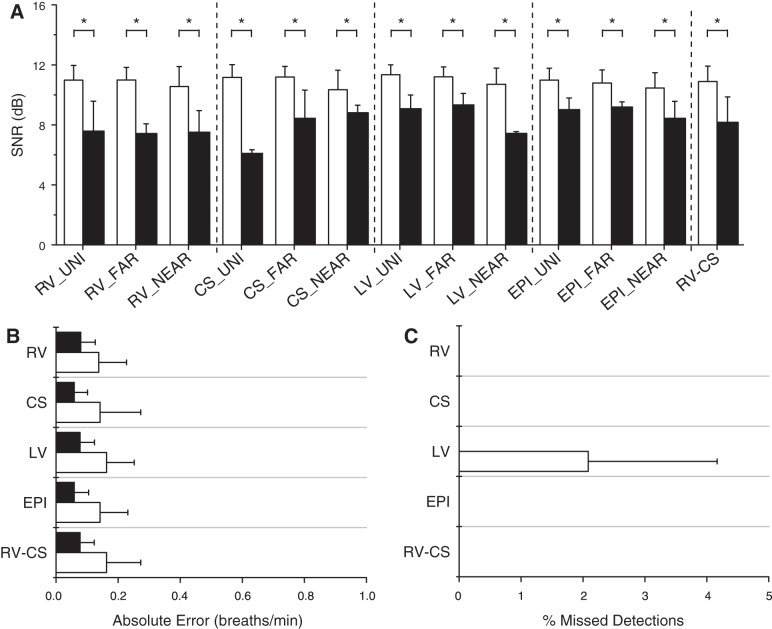
Fig. 5.
Intracardiac lead optimization. A: signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) estimates for every intracardiac lead type, compiled across all animals, at tidal volumes, and ventilation rates, for all accurate (white) and missed (black) detections. The accurate detection SNR is significantly larger than the missed detection SNR for every lead type (*P < 0.001). Across all lead types, the average accurate detection SNR is 11.0 dB, and the average missed detection SNR is 8.2 dB. B: absolute error (means ± SD) for RV, CS, LV, EPI, and RV-CS lead groupings using our optimized algorithm, at tidal volumes of 500 and 750 ml, averaged across all animals. All intracardiac leads are grouped by catheter type, and for each group, the lead combination with the highest SNR at each ventilation rate was used to estimate the RR. The absolute error ranges from 0.09 to 0.16 breaths/min with mean 0.13 breaths/min. C: percentage of missed detections (means ± SD) for each lead group, at tidal volumes of 500 and 750 ml, averaged across all animals. The percentage of missed detections ranges from 0.0 to 2.1%, with mean 0.2%. There were no missed detections using the RV, CS, EPI, and RV-CS leads, while the only missed detection came from a single RR measurement in a single animal at tidal volume of 750 ml in which the maximum SNR was <7 dB for the LV lead grouping.