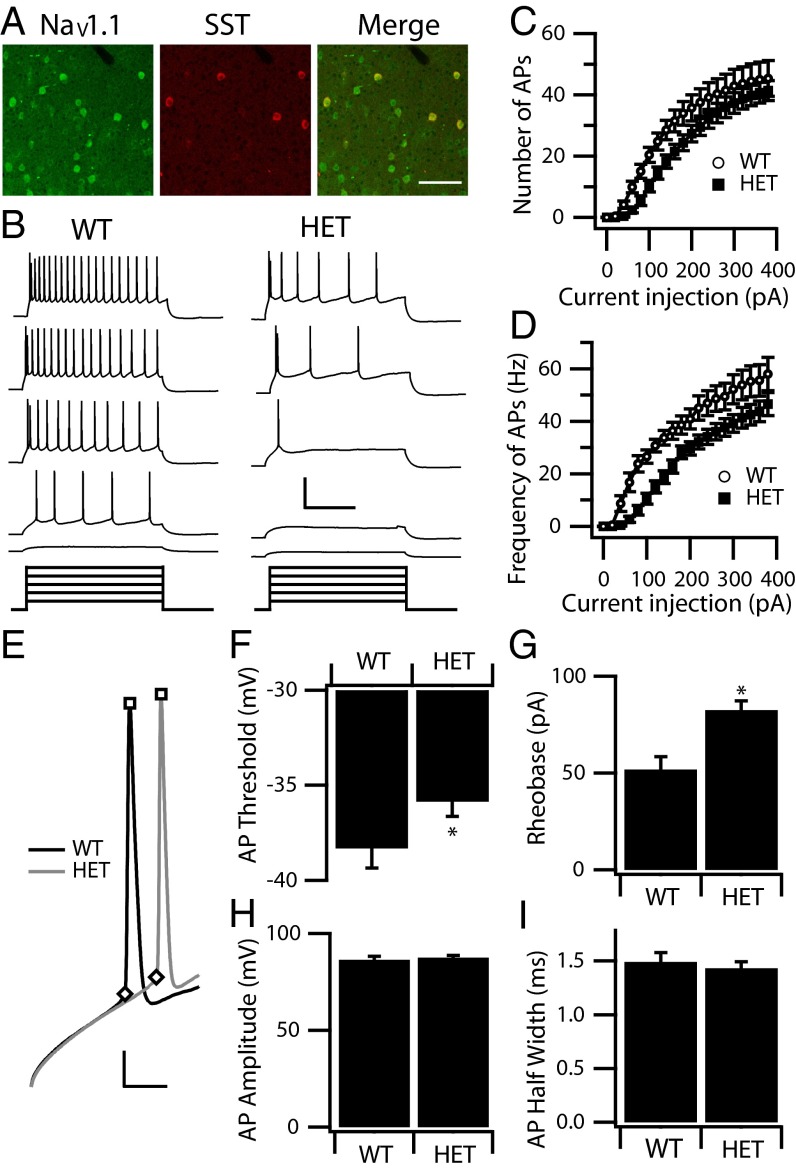
Fig. 4.
Excitability of cortical layer V SST interneurons. (A) Cortical layer V SST interneurons were double labeled with anti-NaV1.1 (green) and anti-SST antibody (red) to show the presence of anti-NaV1.1 channels in SST interneurons. The merged image shows double-labeled SST interneurons in yellow. (Scale bar: 100 µm.) (B) Sample traces of whole-cell current-clamp recordings in response to incremental steps of current (1 s, ranging from 40–200 pA) in a WT and a HET SST interneuron. (Calibration: 0.6 s, 60 mV.) (C and D) The mean number (C) and frequency (D) of APs in response to each step for WT (n = 21) and HET (n = 23). Note that HET SST interneurons require larger current injections to trigger spikes. (E–I) Properties of individual WT and HET APs. (E) Expanded and superimposed individual APs from recordings of the WT and HET SST interneurons in B. (Calibration: 5 ms, 20 mV.) (F) Mean AP threshold. (G) Mean AP rheobase. (H) Mean AP amplitude. (I) Mean AP half width. *P < 0.05.