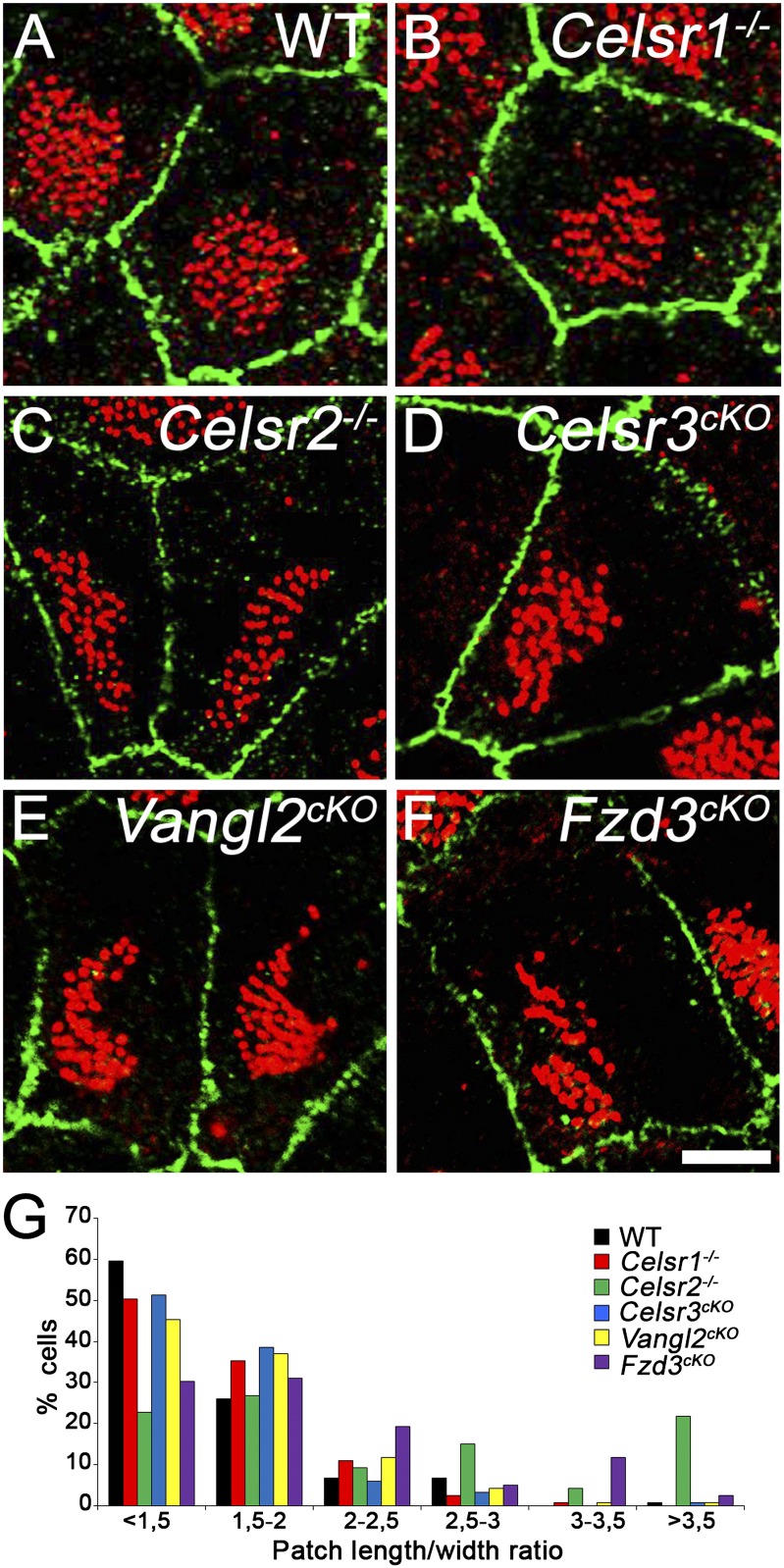
Fig. 2.
The clustering and off-centering of BBs are preserved in PCP mutants. (A–F) P21 cells from (A) WT, (B) Celsr1−/−, (C) Celsr2−/−, (D) Celsr3cKO, (E) Vangl2cKO, and (F) Fzd3cKO stained for ZO1 (green) and γ-tubulin (red). In all genotypes, BBs regroup into off-centered patches that are generally round in WT and Celsr1−/− but exhibit irregular shapes in Celsr2−/−, Celsr3cKO, Vangl2cKO, and Fzd3cKO. Relative distance of displacement calculated as the ratio of the distance between the centers of the apical surface and the patch divided by the distance between the cell center and the membrane: WT: 0.40 ± 0.02, 1,193 cells; Celsr1−/−: 0.38 ± 0.03, P = 0.1859, 1,107 cells; Celsr2−/−: 0.34 ± 0.01, P = 0.0007, 730 cells; Celsr3cKO: 0.38 ± 0.02, P = 0.1764, 439 cells; Vangl2cKO: 0.35 ± 0.02, P = 0.0086, 1,013 cells; Fzd3cKO: 0.34 ± 0.03, P = 0.1559, 557 cells. Five animals per genotype, four animals for Fzd3cKO, and three animals for Celsr3cKO. (G) Distribution of cells according to the patch length/width ratio. Contingency table test compared with WT: Celsr1−/−: P = 0.268; Celsr2−/−: P < 0.0001; Celsr3cKO: P = 0.1831; Vangl2cKO: P = 0.1411; Fzd3cKO: P < 0.0001. One hundred twenty cells for each genotype; three animals per genotype. (Scale bar: 5 µm.)