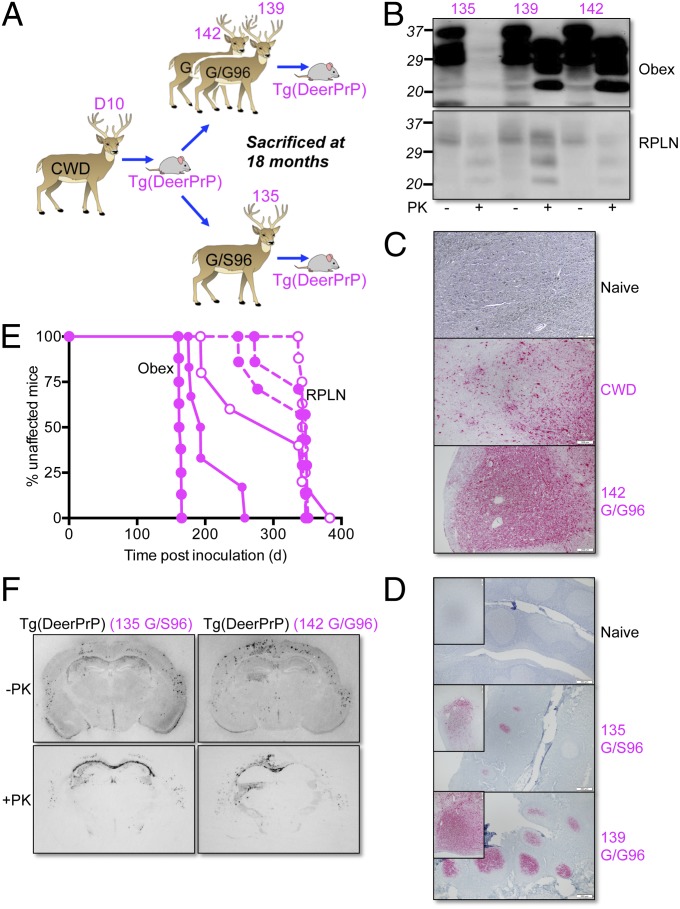
Fig. 4.
Transmission of Tg mouse-adapted CWD prions to deer. (A) Passage history of CWD from D10 CWD deer to Tg(DeerPrP)1536+/− mice and thence to hand-raised white-tailed deer. (B) Western blots showing levels of total PrP and PrPSc in obex and RPLN of autopsied deer at 18 mo. Fifty micrograms of total protein from obex of 139 and 142 was digested; for 135, the amount was 500 μg. Western blots were probed with mAb 6H4. (C) PrPSc deposition patterns in obex assessed by immunohistochemistry. Naive, uninfected deer; CWD, deer infected with naturally occurring CWD; 142 G/G96, deer infected with Tg(DeerPrP)-passaged D10 CWD. (D) PrPSc deposition patterns in tonsil of deer 135 and 139 assessed by IHC. (Insets) Higher magnifications of individual follicles. (Scale bars in C and D, 200 μM.) (E) Survival curves of Tg(DeerPrP)1536+/− mice infected with obex (solid lines) or RPLN (dashed lines). Solid symbols, WT infected deer; open symbols, G/S96 deer. (F) PrPSc deposition patterns assessed by histoblotting in the hippocampus/thalamus of Tg(DeerPrP)1536+/− mice infected with brain homogenates from 135 and 142 deer. Blots were treated with PK as indicated.