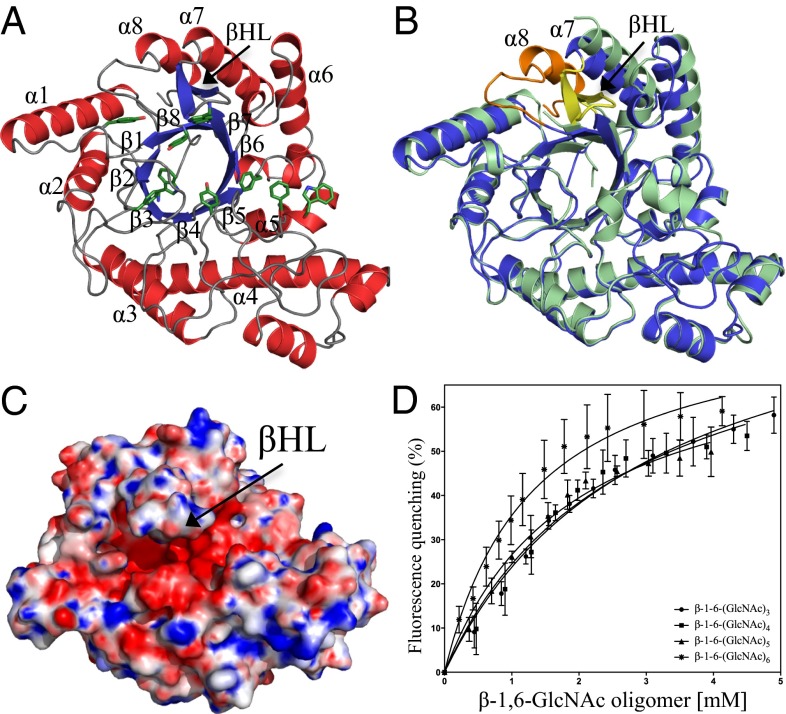
Fig. 2.
Structure of PgaB310–672 and binding of PNAG oligomers. (A) Structure of PgaB310–672 shown in cartoon representation with α-helices and β-strands colored red and blue, respectively, with the canonical (β/α)8 barrel labeled β1–β8 and α1–α8. Aromatic residues that line the groove are shown in stick representation and are colored green. (B) Superposition of PgaB310–672 (blue) and the C-terminal domain of PgaB42–655 (pale green) reveals the final eighth helix of the (β/α)8 barrel fold (orange) and a long βHL (yellow). (C) Electrostatic surface potential of PgaB310–672 shows the βHL extends over an electronegative groove pinching off the binding pocket to ∼7 Å. Quantitative electrostatics are colored from red (−10 kT/e) to blue (+10 kT/e). (D) PgaB intrinsic fluorescence quenching binding curves for titrations with β-1,6-(GlcNAc)3, β-1,6-(GlcNAc)4, β-1,6-(GlcNAc)5, and β-1,6-(GlcNAc)6. Data points are mean values, with error bars representing the SD between triplicate experiments.