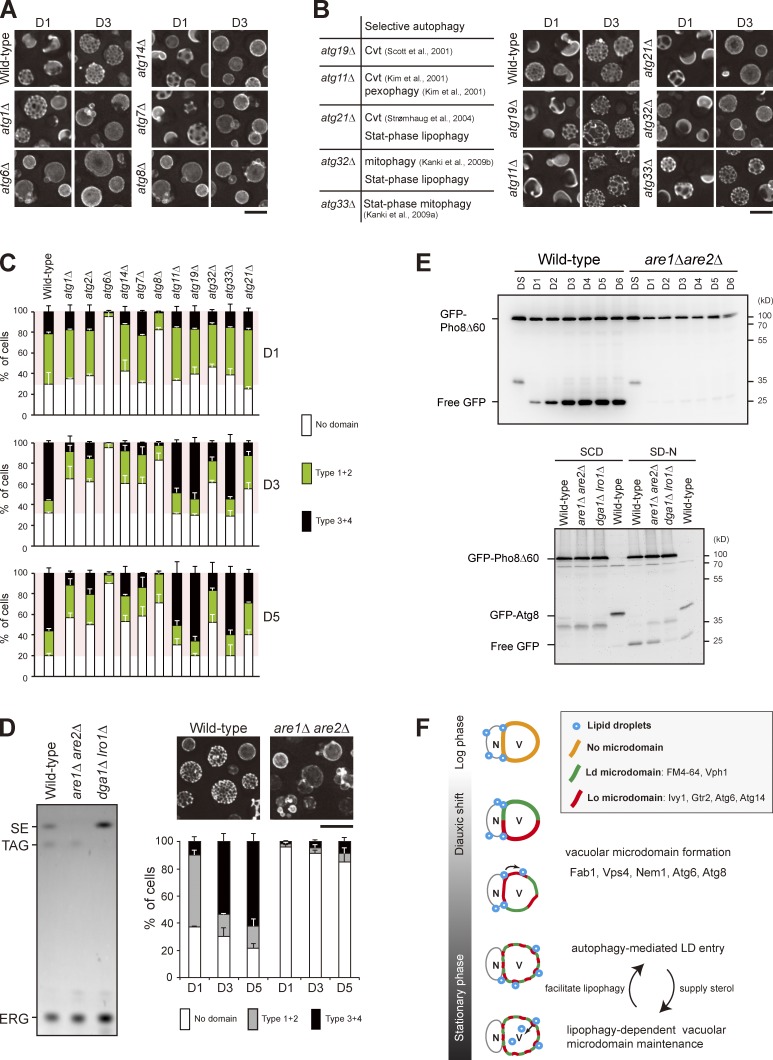
Figure 5.
Stat-phase lipophagy is needed for vacuolar microdomain maintenance. (A) Cells as indicated expressing Vph1-mCherry were imaged by fluorescence microscopy on D1 and D3. (B, left) A table lists selective autophagy defects for the indicated strains. Cvt, cytoplasm-to-vacuole targeting. (right) Same as A. (C) Cells as indicated were quantified based on the Vph1-mCherry patterns and culture conditions as indicated. Data from three independent experiments were plotted as mean ± SD. (D, left) Lipids in strains as indicated were analyzed by TLC. SE, sterol ester; TAG, triacylglycerol; ERG, ergosterol. (right) Wild-type and are1Δ are2Δ cells expressing Vph1-mCherry were imaged by fluorescence microscopy, and three independent data were quantified. Error bars show mean ± SEM from three experiments. (E, top) Cells as indicated expressing GFP-Pho8Δ60 were grown in SC medium to various growth conditions. Cells were lysed, and the lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the anti-GFP antibody. (bottom) Same as top, except that cells expressing either GFP-Pho8Δ60 or GFP-Atg8 were grown in SC medium to log phase (SCD) or shifted to SD-N for 3 h from log phase. (F) Working model for stat-phase lipophagy. N, nucleus; V, vacuole. During DS, vacuolar proteins start to sort into either one of the vacuolar microdomains, Ld or Lo. Several proteins, Fab1, Vps4, Nem1, Atg6, and Atg8, are needed for microdomain formation at the stage. The pattern of quasisymmetrical microdomains appears later in the stationary phase. During this stage, LDs are engulfed by the Lo microdomain and feed vacuoles with sterols to maintain lipid phase partitioning, which in turn stimulates stat-phase lipophagy. Bars, 5 µm.